The outstanding Second World War C.B., 'Southern Desert, Iraq' O.B.E., Great War Fighter "Aces" D.F.C. mounted group of fourteen miniature dress medals worn by Dolphin Pilot Air Commodore F. Woolley, Royal Air ForceCredited with 4 victories, but possibly as many as 8 from July to November 1918, he served as a Special Service Officer with Air Staff Intelligence in Iraq where he spent three years in the desert with Bedouin tribesmen collating intelligenceDuring the Second War he served as Chief Intelligence Officer, Headquarters Mediterranean Allied Air Forces 1943-45The Most Honourable Order of the Bath, Companion's (C.B.) Badge, silver-gilt and enamel; Order of the British Empire, Military Division, Officer's (O.B.E.) Badge, silver-gilt; Distinguished Flying Cross, G.V.R.; British War and Victory Medals 1914-18; General Service 1918-62, G.V.R., 1 clasp, Southern Desert, Iraq; 1939-45 Star; Africa Star with rose on riband; Pacific Star; Italy Star; Defence and War Medals 1939-45; United States of America, Legion of Merit, gilt and enamel, with miniature Star on riband; Belgium, Kingdom, Croix de Guerre, mounted as worn, slight wear to enamel on Order of the Bath, overall very fine (14)His full-size medals sold in these rooms in April 2014.C.B. London Gazette 1 January 1946.O.B.E. London Gazette 3 June 1931. The original recommendation reads:'This Officer has been a Special Service Officer in Iraq since March 1928. Although occupying the most lonely and isolated post in the whole Command, he has consistently displayed, under extremely trying conditions, a tact, patience, and perseverance which are worthy of the highest praise.'D.F.C. London Gazette 3 June 1919.M.I.D. London Gazette 2 June 1943.United States, Legion of Merit London Gazette 27 November 1945. The original recommendation reads:'Air Commodore Frank Woolley, Royal Air Force, as Chief Intelligence Officer, Headquarters Mediterranean Allied Air Forces from February 1943 to May 1945, displayed wise judgment and unqualified devotion to duty in the successful fulfilment of his assignment. Called upon to furnish a synthesis of all intelligence information regarding conduct of operations and to integrate the Anglo-American intelligence structure of the headquarters, he overcame many obstacles to provide source information of high value and veracity and at the same time achieved a smoothly functioning, closely knit intelligence organization. Commodore Woolley's exceptional ability was of great benefit to the conduct of air operations.'Belgium, Croix de Guerre London Gazette 15 July 1919.Frank Woolley was born in Ilkeston, Derbyshire in 1899 and was educated at the County Secondary School. He joined the Army straight from his school O.T.C. on his 18th birthday, and was accepted for a Commission in the Territorial Forces Association. Posted to the 7th Training Reserve Battalion at Rugeley, he subsequently applied to join the Royal Flying Corps, and after initial tutoring at Denham was Commissioned a Second Lieutenant in the R.F.C. on 7 November 1917.Woolley went to France in July 1918 where he was posted to No.1 Aero Supply Depot before receiving his first operational posting on 14 July with No. 79 Fighter Squadron (Sopwith Dolphins), based at St. Marie Cappel east of St. Omer, with whom he fought and flew for the rest of the War. He was without doubt heavily engaged with the enemy for the next four months, '...and the local papers in his home town of Ilkeston credited him with eight victories, and recorded that he himself had been shot or forced down no fewer than three times, evidence of an exciting four months' flying.' (Winged Warriors, Derbyshire Fighter Pilots in World War I, by Barry Marsden refers).His first victory occurred on 27 September, when, according to an account that appeared in the Ilkeston Advertiser, 'he was on readiness at his home base when word was received that an enemy two seater was busy on a reconnaissance over the British front line. He was ordered to intercept the hostile aircraft, and, piloting a Dolphin, sighted it below him somewhere north-west of Armentieres. The first burst from his twin Vickers killed the enemy observer, and the subsequent running battle took both warplanes over the town, where the observation machine suddenly dived away to smash through the roof of a building. When Frank landed back at his home airfield his delighted CO praised his "splendid effort", and promised that "the facts would be reported to the proper quarter".' (ibid). Woolley's own account of the action confirms this: 'I was at 2,000 feet among the clouds South West of Armentieres when I saw a hostile 2-seater, probably an Albatros, about 1,000 feet below me. On being engaged the enemy aircraft dived towards Armentieres. I dived after him and fired two bursts into him at close range. The enemy aircraft spun and crashed into a house in Armentieres.' (recipient's combat report refers).The following day Woolley shot down another aircraft: 'I saw 10 Fokker Biplanes attacking a Bristol Fighter. I climbed into a cloud at 6,000 feet whilst Lieutenant McNeaney attacked the enemy machines. A dog fight ensued in which I saw two Fokkers go down after which Lieutenant McNeaney went down, followed by a Fokker. I attacked this enemy aircraft and fired a short burst at point blank range, and saw him go down and crash.' (Ibid).A month later on 26 October, Woolley despatched an L.V.G. two-seater at 3,000 feet south-east of Renaix before recording his final confirmed victory on 4 November, when 'at 9,000 feet I spotted a Halberstadt two-seater working over Renaix. I flew north and then east and so got east of him and in the sun. I then dived on the enemy aircraft who turned west and then north. I fired a burst at very close range. The enemy aircraft went into a vertical dive and crashed in a gulley between Sulsique and Renaix.' (Ibid).After the Armistice Woolley took up adjutant duties with the Squadron and became a Flight Commander, the Squadron became part of the Allied Occupation Force in December and moved to Cologne. Here he accepted the opportunity to fly numerous surrendered German aircraft, including Fokker DVIIs, Rumplers, and Halberstadts. Whilst stationed in Germany he learnt of the award of his D.F.C. and also received the Belgian Croix de Guerre, having the latter pinned on his chest by King Albert himself. He transferred to the unemployed list in October 1919, but was recalled to a short-service Commission the following June and served at R.A.F. Lee-on-Solent and Calshot. Qualifying as a pilot flying seaplanes and multi-engined flying boats, he fell in love with the Solent area, and wrote to tell his fiancée: 'I am sure that you will love this place too, and if I live long enough to retire this is where we shall live.'Southern Desert, Iraq - With the BedouinIn July 1927 Woolley was appointed to a permanent Commission in the General Duties branch of the Royal Air Force and, having been promoted Flight Lieutenant in January 1928, he embarked upon a course in Arabic at the School of Oriental Studies in London. After completing the course in March he was immediately posted to HQ Iraq as a Special Service Officer with Air Staff Intelligence, and for the next three years was responsible for the collection of intelligence in the vast unmapped desert west of Basra, spending the time living with the Bedouin tribesmen, 'sharing the hardships of their primitive, nomadic lifestyle, enduring searing heat, frequent dust and sandstorms, plagues of flies, and living off revolting food and foul water.' (Win…
We found 31238 price guide item(s) matching your search
There are 31238 lots that match your search criteria. Subscribe now to get instant access to the full price guide service.
Click here to subscribe- List
- Grid
Sold by Order of a Direct DescendantThe unique and superbly well-documented 'Far East Communication Squadron 1950' A.F.M. group of seven awarded to Master Signaller J. B. C. Browne, Royal Air Force, who was awarded his Nuclear Test Medal for the 'Christmas Airways' flights to Christmas Island during Operation GrappleBrowne's remarkable career saw him flying during the Second World War, earning his A.F.M. in the east for flights which included missions to China redacted from his service papers and flying the Royal Couple during their 1961 Royal Tour of NepalAir Force Medal, G.VI.R. (571907 Sig. I. J. B. C. Browne. R.A.F.); 1939-45 Star; Defence and War Medals 1939-45; General Service 1918-62, 2 clasps, Malaya, Arabian Peninsula (571907 Sig. I.A. J. B. C. Browne. R.A.F.), the second detached in its named box of issue; Royal Air Force L.S. & G.C., E.II.R. (M. Sig. J. B.C. Browne. (571907) R.A.F.); Nuclear Test Medal, unnamed as issued, the first six mounted as worn, the last in its named box of issue, sold together with a large archive including the recipient's flying log books, minor contact wear to sixth, overall good very fine (7)A.F.M. London Gazette 8 June 1950, the original recommendation states:'Signaller I Browne joined the Squadron in October, 1948, having been in Japan from October, 1947, and has been employed as a V.I.P. Signaller. He is a first class non-commissioned officer with exceptional technical ability, having consistently held an 'A' category since August, 1946. During the last six months he has completed 300 flying hours on some of the most important flights assigned to this Squadron, and he has also extended his 'A' category to cover York aircraft as well as the Dakota, the type in which he is primarily signaller and, on numerous long distance flights during his tour of duty in the Far East Communication Squadron, he has carried out his duties in an exemplary manner. He has shown ability, coolness and enthusiasm and is an outstanding non-commissioned officer.'Note the Recipient's Flying Log Book for the period of 1947-1952 is missing, it is believed to have been recalled owning to a redacted mission in China rather than misplaced or lost.John Blake Cameron Browne (who later changed his surname to Howard) was born in Kensington, London on 19 February 1922, the son of Andrew and Wilhelmina 'Billy' Browne. His father was a former professional soldier who served as a Sergeant-Major with the Essex Regiment and was seriously wounded in the leg at Gallipoli. He appears to have suffered from post-traumatic stress disorder and left the family in 1929 leaving his wife to raise the children herself. The young Browne received only a basic education however this was enough for him to pass the entrance tests for an apprenticeship at R.A.F. Halton on 24 August 1937.He was initially posted to the Electrical and Wireless School before transferring to No. 2 Wireless School on 26 March 1938. He must have proven himself a quick learner as he was soon selected to leave Halton for Cranwell, where he specialised as a Signaller. He was still there on the outbreak of the Second World War on 3 September 1940, they spent the day dispersing the aircraft around the perimeter of the airfield in case of air raids.The Second World WarQualifying as Wireless Electrical Mechanic on 29 January 1940, Browne reached his majority the next month on 19 February and was appointed Aircraftman Class I the same day. Posted first to No. 29 Squadron and advanced Leading Aircraftman on 1 April 1940 he served with them at R.A.F. Digby. Here he was on the receiving end of several bombing raids, being promoted Corporal on 31 December 1940. The Squadron re-equipped with Bristol Beaufighters to replace their old Blenheims not long later.Transferring to R.A.F. Pembury he undertook an air gunner's course, becoming qualified on 6 January 1943 and advanced Sergeant on 7 January. Joining No. 10 Radio School Carew Cheriton, he served there until 17 February 1943 when he was posted to Coastal Command's 131 Operational Training Unit which was located on Loch Erne in Northern Ireland. There he had his first flight on a Catalina flying boat on 18 February.Having qualified, Browne was posted to the newly formed 265 Squadron based in Northern Madagascar. After a gruelling journey across Africa, he finally reached the posting in early June and began to undertake fleet escort and search and rescue missions as Wireless Operator/Air Gunner. Racking up increasing Operational flying time in December he had 250 hours and was advanced Flight Sergeant on 6 January 1944.Over the next year he was to continue in this role, adding Meteorological Flights to his duties. The last of Browne's wartime flying was with 265 Squadron having undertaken 562 hours of Operational flight with them and an impressive 1076 hours in total. Posted to R.A.F. Wymeswold on 5 May 1945, he arrived on 8 May - V.E. Day - to discover the station all but deserted, the guard on the front gate informed him that everyone was celebrating in the pub.V.I.P. Flying, a Redacted Mission and a Crash LandingBrowne retrained with Douglas Dakotas and was soon posted to 147 Squadron, flying for Transport Command. This Squadron flew from Britain to Europe allowing Browne to assemble a collection of European banknotes which he stuck into his log books.Joining 24 Squadron for V.I.P. transport flights in October 1946 he was posted to the British Commonwealth Air Force in Japan the following year. The next year Browne again moved, this time to the Far East Communications Squadron. Two months after he joined them a period of one week on his service records is redacted, this combined with his missing log book covering this period is suggestive of a clandestine mission. The cataloguer must leave it to the reader to imagine the nature of this work however it occurred at a time that Browne was known to have been flying to China, then embroiled in the Civil War.Returning to Britain in April 1950 he was awarded the Air Force Medal at R.A.F. North Luffenham for his work with the Far East Communication Squadron. His work there had also entitled him to the Malaya bar for his General Service Medal however this would not be issued at the time and Browne was to receive the G.S.M. for a separate campaign. Joining 242 Operational Conversion Unit as a Trainer and he was recommended a Commission at that point however he rejected the offer, feeling that he preferred his role as a Warrant Officer.Returning to No. 24 Squadron on 6 December 1953 he rang in the new year with a promotion to Master Signaller on 31 December. One of his early flights here on 22 May 1954 was transporting Anthony Eden (then Foreign Secretary) and Lord Ismay (then Secretary General of Nato) from Geneva to Paris and thence to Britain. A further flight in July almost led to disaster as the crew lost their way between Suffield, Alberta and Britain. An S.O.S. signal was sent out and after a tense period of waiting were picked up by a passing liner which was able to give them their co-ordinates, with their available fuel they were just able to make an emergency stop at the Azores Islands.That same year he performed trips to Australia which included the transport of material and personnel involved in the developing Nuclear programme. During one routine training mission the next year out of R.A.F. Abingdon the Hastings aircraft Browne was flying in crashed on landing. Fortunately the crew were all unharmed although the aircraft itself lost a wing. The next year he transferred to No. 47 Squadron flying mostly to the Middle East, Cyprus and Malta.Christmas Island Airways and Operation GrappleBrowne had alr…
The 1916 D.C.M. group of four awarded to Corporal H. W. Lane, Grenadier Guards, later 4th Battalion, Guards Machine Gun Corps, a former footballer who served in France from the start of the war but was tragically killed in action on 30 March 1918Distinguished Conduct Medal, G.V.R. (15585 Pte H. W. Lane. 1/G.Gds:); 1914 Star (15585 Pte H. W. Lane. 1/G. Gds:); British War and Victory Medals (15585 A.Cpl. H. W. Lane. G.Gds.), good very fine (4)D.C.M. London Gazette 14 November 1916, the original citation states:'For conspicuous gallantry in action. He led his machine gun team forward with great courage and determination, reaching the second objective. Later, he pushed on to the third objective and accounted for large numbers of the enemy.'Henry William Lane was born at Bristol and enlisted at Cardiff and entered the war in France on 8 November 1914 with the 1st Grenadier Guards. The unit saw fighting at the First Battle of Ypres before being involved in the bloody Battle of Neuve Chappelle in March 1915, a newspaper article written at the time quotes a letter Lane wrote to his family about the engagement stating:'Gloucester Grenadier at Neuve ChapellePte. Harry Lane, 1st Grandier Guards, eldest son of Mr. and Mrs. W. H. Lane, Elmbridge road, Barnwood, writes under date March 15th as follows: "Well, we have been in a big action and thank God I got through all right. Sorry to say we lost heavily, but we beat the Huns, and got the position we fought for. You will have read about it by this time. The artillery fire was terrible, but the boys stuck it as they always do, and we have the devils more than they bargained for." Pte. Lane is an old footballer, and played for Barnwood and the City A Team.'A letter written by Major Christie R.A. in The Daily Mail adds:'The fighting about Ypres was of the most desperate description. It was there I saw the Guards go into action, and it was there, I may tell you, that these Regiments - the Coldstream Guards, the Grenadier Guards, and the Scots Guards - covered themselves with imperishable glory, and accomplished what I believe is held to be one of the finest military feats of the war.'Lane continued to serve with them until the formation of the Guards Machine Gun Corps on 1 March 1918. Posted to the 4th Battalion, Guards Machine Gun Corps he was stationed with them when the unit was posted to the front to try and stem the German Spring Offensive. Thrown into the Battle of Saint-Quentin on 21 March they were still engaged on 30 March 1918 when Lane was killed in action. He is buried at Bucquoy Road Cemetery, Ficheux.Letter to his mother from a Lieutenant Commanding a gun team in his Company states:'I hope you will accept my heartfelt sympathy in the loss of your husband, Corporal Lane, who was in Charge of one of my guns teams when he was hit with some others in a deep dugout. He was killed instantaneously with five others by a fearfully unlucky shell which came straight down the mouth of the dugout.I am not saying it for the sake of talking but your husband was held in the highest esteem in this Company and for myself I was proud of having such a good soldier with me.'Sold together with original letters and cards, newspaper cuttings, two photographs and a Commonwealth War Graves Cemetery Register with Corporal Lane's details.…
The 1918 D.S.O. group of seven awarded to Lieutenant-Colonel R. S. Hunt, 1st Dragoon Guards, late 3rd Hussars, who was twice wounded in action and twice 'mentioned' during the Great WarDistinguished Service Order, G.V.R; Queen's South Africa 1899-1902, 3 clasps, Orange Free State, Transvaal, South Africa 1902 (Capt: R. S. Hunt, 3/Hrs:); 1914 Star, with clasp (Major R. S. Hunt. 1/D.Gds.); British War and Victory Medals (Lt. Col. R. S. Hunt.); General Service Medal 1918-62, 1 clasp, Iraq (Major R. S. Hunt.); Delhi Durbar 1911, unnamed as issued, light contact marks, very fine overall (7)D.S.O. London Gazette 1 January 1918.Ronald Seager Hunt was born on 24 February 1874, the son of Walter and Alice Hunt of Hart Hill, St. Johns, Woking, where his father worked as a barrister. Educated at Haileybury College (1888-1892), he was commissioned 2nd Lieutenant on 25 November 1893 with the 3rd Battalion Norfolk Regiment. Transferring from the Militia to the 3rd Hussars on 15 May 1897 with the same rank he was advanced Lieutenant on 13 September 1898.Prior to his service in the Boer War, Hunt was advanced Captain on 26 April 1901 and arrived in South Africa in January 1902. There he was present for operations in the Transvaal and Orange River Colony until 31 May 1902. Whilst there the Regiment saw notable action in an engagement on the Cornelius River in February 1902.Transferring to the 1st Dragoon Guards, Hunt was promoted Major with them on 14 July 1910. The next year he appeared upon the roll of the Delhi Durbar 1911 medal as one of three Majors with the unit.Entering the war in France on 5 November 1914 he appears to have served initially with his own unit however was soon posted to command several different Infantry Regiments, including at some stage the 4th Battalion, Seaforth Highlanders. Hunt later commanded the 8th Battalion, Royal Lancaster Regiment from 27 October 1916, being stationed with them on 6 February 1917 when he was wounded for the first time.Wounded in action again during the Battle of Arras on 11 April 1917, he received his first 'mention' at the end of that year (London Gazette 11 December 1917). Unfortunately his age caught up with him and Hunt was posted to command the 87th Battalion, Training Reserve on 10 May 1918, receiving his second mention ten days later, likely for his final actions with the Lancaster Regiment (London Gazette 20 May 1918).Posted to command 1st County of London Yeomanry on 13 September 1919 he served for two more years but eventually retired on 17 September 1921 to Walcott-on-Sea, Norfolk. Hunt died on 1 April 1942.…
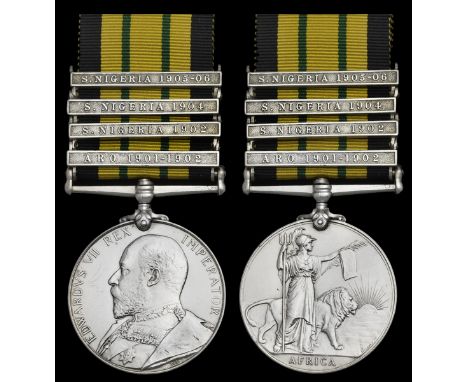
The Zulu War Medal awarded to Private H. Muldowney, Army Hospital Corps, who is understood to have been wounded in action at the Battle of Bronkhorstspruit in December 1881, during the First Boer WarSouth Africa 1877-79, 1 clasp, 1879 (3891. Pte. H. Muldowney. A.H.C.), contact marks overall, nearly very fineHarry Muldowney was born St Faith, Winchester in 1860 and enlisted in the Army Hospital Corps in 1878. Having served in South Africa, he saw further active service in the Egypt & Sudan 1882-89 campaign.… SALE 25001 NOTICE:Gold match safe weighs 34g. Naming of the Aero Club of America Medal now added to the Lot.
Pair: Major-General R. Ranken, 35th Madras Native Infantry, whose combination of awards is unique to the regimentIndia General Service 1854-95, 1 clasp, Pegu (Captmn. Robt. Ranken. 35th. Regt. M.N.I.); Indian Mutiny 1857-59, no clasp (Capt. R. Ranken, 35th. N.I. S.A.C.G.) both with decorative silver top riband bars, light contact marks, nearly extremely fine (2)Note a unique combination to the 35th Madras Native Infantry.Robert Ranken was born in Brechin, Forfar on 30 October 1822 and was educated at Perth Academy. Nominated as a cadet for the Honourable East India Company's Madras Infantry by Company Director John Shepherd at the recommendation of the Earl of Stair, and was commissioned Ensign on 12 June 1841, joining the 35th Madras Native Infantry.Seeing little action for the first decade of service Ranken was promoted Lieutenant on 1 May 1844, and Captain on 29 November 1849. Still serving with the Regiment during the start of the Second Anglo-Burmese War he was with them at the capture of Ilangonn and Rangoon in April 1852. Later in the year the unit was involved in the hunt for the fugitive Governor of Rangoon and finally the capture of Prome in October 1852. Ranken saw further fighting in the country during the capture of Meeaday in January 1853 and several other minor actions.Still serving as a Captain on the outbreak of the Indian Mutiny some five years later Ranken was stationed with the Sauger Field Force as Executive Commissariat Officer under General Whitlock. This was swiftly followed on with the appointment of Assistant to the General Superintendent of Operations for the suppression of the Thuggee and Dacoity groups operating in the Jubbulpore District on 8 June 1860.Transferring to the Madras Staff Corps on 18 February 1861, he was advanced Major on 12 June of that year and passed his examinations as an interpreter in Hindustani and Persian by 1865. Further appointed Superintendent of the Jubbulpore Central Jail in May 1866 and was promoted Lieutenant-Colonel on 12 June 1867 and further advanced Colonel on 12 June 1872.He retired to Mortlake, Surrey with the honorary rank of Major General on 9 June 1877, and died at his home in Upper Norwood on 8 March 1895, aged 83; sold together with copied research.… 25001 SALEROOM NOTICE:Lot is NOT subject to 5% Import Tax.
Pair: Private E. B. Fisher, 9th LancersPunjab 1848-49, 2 clasps, Goojerat, Chilianwala (E. B. Fisher, 9th Lancers); Indian Mutiny 1857-59, 3 clasps, Delhi, Relief of Lucknow, Lucknow (E. B. Fisher, 9th Lancers), minor contact wear and edge nicks, otherwise overall good very fine (2)Edward Bird Fisher was born at St. Michael, Beccles on 5 December 1821 and attested for the 9th Lancers in London on 1 December 1845. His service papers note that during the Punjab Campaign he was present for the Passage of the Chenab on 4 December 1848 and the Battles of Chillianwala and Goojerat. In the former they were one of the Regiments that did not break and instead managed to prevent the Sikh forces from turning General Gough's flank.Fisher was still with the Regiment on the outbreak of the Indian Mutiny, serving in Captain Drysdale's 'B' Troop. Their first action was the Battle of Badli-ki-Serai on 5 June 1857, which helped to clear the way to Delhi. They were present throughout the siege itself and were present for the capture of the city on 14 September.Fisher saw further action at Boolundshuhur, Alligurh and Agara as well as actions at Kanoge and Mariagung. The Regiment later joined the Army under General Sir Colin Campbell being assembled to retake Lucknow, and were present for the destruction in of the Gwalior Contingent at Cawnpore and Seria Ghat in December.They started the next year with action at Shumshabad in January 1858 during the advance on Lucknow. The 9th were present for the final recapture of Lucknow in March, as well as actions at Allegunge, Bareilly, Shahkehanpore and Mahomadee. They closed out the war with service in the Central India Campaign being present at the passage of the Gogra, the affair at Mulchlegaon and Kumb-da-Kote between 1858-59.Fisher was finally discharged on 29 February 1860 after seeing 13 years and 6 months service in India. He joined the Metropolitan Police on 11 June 1860, serving with the Holborn Division until 10 July 1878 and died on 15 March 1879; sold together with copied service papers.…
The superb posthumous 'Amiens 1918' M.M. awarded to Corporal W. H. Bowen, 19th Battalion, Australian Infantry, who saw service at Gallipoli, was four times wounded, and finally killed in action at the time of earning his decorationMilitary Medal, G.V.R. (1149 Cpl H. W.Bowen. 19/Aust.Inf.), very fineHerbert William Bowen was born in Sydney, New South Wales, Australia in 1888 and enlisted on 10 March 1915 with the Australian Imperial Force. Posted to the 19th Battalion Bowen embarked with them on 25 June 1915 for Gallipoli where they formed part of the first wave of reinforcements after the initial landings. The unit landed on 21 August and were immediately thrown into the Battle of Hill 60, Bowen appears to have passed through this unscathed however he was wounded on 1 September 1915. A telegraph sent to his wife confirming this notes that it was not reported to be a serious wound.Joining the evacuation of the Peninsula the Battalion was posted to the B.E.F. in France on 18 March 1916. They were soon in action during the Battle of the Somme at the bloodily contested front of Pozières, here the Australian 1st Division suffered over 5,000 casualties before eventually being relieved. Bowen was wounded here suffering multiple gunshot wounds on 28 July and being treated at the 44th Casualty Clearing Station before hospitalization.Rejoining his unit on 9 April 1917 after an extended rehabilitation in England he served without incident for the rest of the year during which time the Battalion saw action at Bullecourt and Passchendaele. In the effort to resist the German Spring Offensive however he was again on the frontline and was gassed on 28 May 1918, necessitating another recovery process.Finally returning to his unit on 13 July 1918 Bowen joined the action on 11 August 1918 during the Battle of Amiens. After his act of gallantry he was again wounded in action, the witness statement of Private H. S. Doohan, quoted in his service papers gives further details, stating:'I saw Cpl. Bowen. D. Company. after he was wounded (think arm) at Framerville about 5 or 6 a.m. I was a runner and was going up to the position when I saw him. He called out as he passed me on his way back to R.A.P. He was a walking case. I did not see anything more of him. He had to go through the orchard to get to the Aid post and the shelling was very heavy. Bowen was big, broad, fair, reddish complexion, about 33 years.'Bowen is commemorated upon the Villers-Bretonneux Memorial; sold together with copied research.…
The 'Post-War' R.R.C. group of six awarded to Matron E. Prescott, Queen Alexandra's Imperial Military Nursing Service, who was further 'mentioned' for her services in Sicily in March 1944Royal Red Cross, 1st Class (R.R.C.), silver-gilt and enamel, the reverse officially dated '1949', mounted for wear upon a lady's bow riband in its fitted Garrard & Co. box of issue; 1939-45 Star; Atlantic Star, clasp, France and Germany; Africa Star, clasp, North Africa 1942-42; Italy Star; War Medal 1939-45, with M.I.D. oak leaf, mounted as worn, sold together with original material including the R.R.C. slip of issue named 'Matron E. Prescott, R.R.C.' and the envelope of issue named to the same, overall nearly extremely fine (6)R.R.C. London Gazette 1 January 1949.Ethel Prescott was born at Lund near Driffield, East Riding, Yorkshire on 22 October 1893, the daughter of Thomas and Jane Prescott. She was educated at Dame Chatterton's School for Young Ladies, North Dalton and after a brief spell as a housekeeper she went to train as a nurse with the Royal London Hospital.Qualifying as a state registered nurse and midwife she joined Queen Alexandra's Imperial Military Nursing Service on 15 August 1927 at Shorncliff, Kent as a Staff Nurse. Posted to India, Prescott was stationed at Rawalpindi in 1928 and saw a further six years of service on the subcontinent with postings at Murree, Peshawar, Nowshera and Quetta.Returning to service as a Sister on 30 May 1941, her first wartime posting was the Hospital Ship H.M.H.S. Aba. Later posted to South Africa she served at Pietermaritzburg in 1943 before being transferred to service in Italy. It was here that Prescott was 'mentioned' (London Gazette 23 March 1944, refers) before being posted to New York with the rank of Matron swiftly following.She remained in North America and Britain between 1944-45 before finally returning to the front in Germany in 1945. Prescott served in Burma in 1946 and finally at Wheatley in a hospital well known for its treatment of head injuries.After the war Prescott went on to serve as Matron at Dulverton Hall, Scarborough, a home for retired clergymen. Her medals were sent to her on 31 August 1948 at The Woods, Beckingham, Doncaster and she retired from Queen Alexandra's Imperial Military Nursing Service on 22 October 1948 with the rank of Honorary Principle Matron. She was admitted into the Royal Red Cross the next year, her award was sent to her at 72 Greengate, Malton, Yorkshire.Sold together with copied research and an original archive comprising a named slip of issue for the R.R.C., photograph of the recipient in uniform, newspaper cutting announcing the award, box and addressed envelope of issue and corresponding riband bar for the campaign medals.…
The 'Tail End Charlie's' D.F.M. group of six awarded to Sergeant R. A. Norcross, Royal Air Force Volunteer Reserve, who downed a FW.109 over HungaryDistinguished Flying Medal, G.VI.R. (1589610 Sgt. R. A. Norcross. R.A.F.); 1939-45 Star; Africa Star; Italy Star; Defence and War Medals 1939-45, mounted court-style for wear, minor pitting, very fine (6)D.F.M. London Gazette 7 July 1944, the original recommendation states:'Sergeant Norcross was posted to this unit in November 1943, and has completed 20 Operational sorties over Italy, Yugo Slavia, Austria and Bulgaria.2. Sergeant Norcross is the rear gunner in a crew which has already carried out many successful operational sorties, and has achieved a high standard of crew co-operation. He is a keen and efficient Air Gunner, and had the complete confidence of his captain and the other members of the crew.3. On the night of 3rd April 1944, Sergeant Norcross had an opportunity of proving his alertness and efficiency when his aircraft had been ordered to attack the [M]anfred Weiss Works at Budapest. Shortly after leaving the target, two enemy aircraft were encountered. One of these aircraft, identified as a FW.190, fired a short burst of tracer at the Wellington, which turned to starboard. The enemy aircraft then continued its course, and passed approximately 20 feet under the Wellington's port Wing. Sergeant Norcross had been told over the intercom. that the FW.190 was "coming up on port at 300 yards 8 o'clock". He fired a three second burst with the FW.190 dead in his sights, and saw it burst into a blue white flame, descending then in a vertical dive. Several other Wellington crews saw the enemy aircraft crash, and Group have officially admitted the claim of one FW.190 destroyed.4. The above incident well illustrates the alertness and efficiency which Sergeant Norcross has displayed in all his operations. His action was typical of the manner in which he invariably carries out his work, and it is submitted that he well deserves the immediate recognition, which is strongly recommended.'Ronald Albert Norcross was serving with No. 37 Squadron based in Southern Italy when he won his award. They completed a number of missions from that region, notably helping to supply the Yugoslavian Partisans resisting German occupation and disrupting their supply routes to the Eastern Front.He was notably present on a raid on 20 January 1944 over the Cecina Railway Bridge in Tuscany. The raid was largely successful except for Norcross' own aircraft, commanded by Flying Officer Stanton, the Squadron Operations book notes:'F/O Stanton in "V" collided with another aircraft ("A" - F/Sgt. Kelly) over the target area but neither aircraft sustained very serious damage.'Despite this Norcross's Wellington found the bombing mechanism damaged, leaving them unable to complete the attack. During the attack over the Manfried Weiss works several months later fifteen Wellington's targeted Budapest to good effect but encountered heavy resistance as the Operations Book makes clear, stating:'The target was well defended, both from the ground and in the air, and moderate to intense H.A.A., and intense L.A.A., with "flaming onions" and 15-20 searchlights were reported. Several enemy fighters were seen in the target area, and one aircraft, captained by F/O Stanton, shot down a FW.190 over the target.'The official recommendation was seconded by The Officer Commanding No. 231 Wing who added his own opinion, stating:'I consider that the coolness and courage displayed by this N.C.O. was largely responsible not only for the destruction of an enemy aircraft but also for his own crew's and the aircraft's safe return to base.'Sold together with copied research.…
An outstanding 'Trench Raid' M.C. group of eight awarded to 2nd Lieutenant J. F. Thoburn, 13th Battalion, Rifle Brigade, later Lieutenant-Colonel, Royal Army Service CorpsThoburn was photographed alongside his comrades before going into action and also wrote at length regarding the action which won his decorationMilitary Cross, G.V.R.; British War and Victory Medals (2. Lieut. J. F. Thoburn.); 1939-45 Star; Africa Star, clasp, 1st Army; Defence and War Medals 1939-45; Efficiency Decoration, Territorial, G.VI.R., reverse officially dated '1947', good very fine (8)M.C. London Gazette 11 January 1919:'When the enemy, in a determined counter-attack, gained a footing in our trenches this Officer led his men over the top and attacked those who had got through the wire, killing several, dispersing the remainder, and capturing a machine-gun and trench mortar. The confidence inspired in his men by his example restored a critical situation.'Jack Fancourt Thoburn enlisted into the Honourable Artillery Company on 17 April 1916 and served in France with the 3rd Company, 2nd Battalion (as No. 7455) from 18 November 1916. Sharing in the action at Bucquoy in February 1917, he was wounded in action. Thoburn was subsequently commissioned 2nd Lieutenant into the Rifle Brigade, serving with the 13th Battalion in France from March 1918. He earned his outstanding M.C. for his actions on 12-13 September, when a Trench Raid captured the enemy positions around Havrincourt Wood. Poison shells were sent down and a heavy counter came the following evening. Thoburn was photographed with his comrades before going into action and also wrote of his experiences:'I am off in an hour's time to the line, Captain Jenkins and Wallis are going with me for which I am awfully glad. We three are great chums. You know that since I have been a soldier I have passed through some awfully rough times and most trying experiences, especially in the earlier stages of the war, and I am by now pretty used to being knocked about : but going again into the thick of the fighting gives one a strange sensation - an indescribable feeling - going up to face death, but one must not think of that, the same Mighty Power that kept me all through those awful Somme battles, can still keep me. I'm just going to do my duty to the very best of my ability - my safety lies in Higher Hands. God knows what I have done in the last few days. I must tell you a little of what I have been doing, in myself I am quite fit, but very tired. My hands are cut up with innumerable cuts, my feet are shooting with pain from not taking my boots off for so long, but we are all in the same boat and are feeling quite happy. It is a lovely sunny day and quite warm, all our company officers are squatting outside our little dugout writing home.Now as some time has elapsed since these episodes, I think I can give you a few details of my adventures without in any way falling foul of my duties as a censor. One comes to my mind - We were leading the Company up, preparatory to "going over the top". Wood (the Coy Commander) and myself were trying to find our way in a wood, it was pitch dark. Wood went first and he suddenly disappeared, the next moment I followed him, falling about twenty feet through bushes, thorns and brambles. At the bottom I stumbled to my feet, breathless with the fall and choked with the gas from the shells that the Boches were firing around us. I heard Wood's voice for a moment and then I lost him - I got caught among the barbed wire - round and round I ploughed until I heard to my immense relief Davis' voice. We lay there together, our men just behind us waiting for the moment. Just like a cyclone it came, with one terrific roar our barrage breaks - then clear and distinct above the rumble of the guns came the sharp crack of the Machine guns - then over we went, and did some quick work. The prisoners came trooping up in groups. I came upon a party of young boys, they were terror stricken - up went their hands the moment they saw me and actually cried like babies. Two of our officers were killed, it was awfully hard luck, they were both such jolly good chaps, one of them was married. In consequence of their death, Hunter and I went to their company to help them and which meant we were very unfortunate, because we had to do the work of both companies. When "C" Coy was in, we were, and when "D" Coy was in, we were also, getting no respite from fighting.I enclose two ribbons - the black and white is the Iron Cross, the other ribbon is foreign, probably Turkish. I cut them from the tunic of a Boche Machine gunner - with his gun he held me up for some time doing a good deal of damage. He it was who killed our two officers, anyhow he was dead when I got up to him and these ribbons were his decorations; he was an intelligent looking fellow and looked quite peaceful in death.In one of the captured trenches we had a meal off German bread and sausage, the bread was damp, heavy and nearly black - the sausage reminded me of the German Mail and their uncooked dainties. Some tried the Boche wine, but the general verdict was that it was like methylated spirits. We found some good cigars and it was really amusing to see all our men swaggering about with cigars in their mouths. But there was more serious work ahead. The afternoon of the attack I had come off duty in the advance line and was lying down at Coy Headquarters - when there was a cry, "the Boches are coming", I sprang up and rushing along by a way that I know, gained the front line. There I found Hunter with some men retiring down the trench and some twenty yards away the Germans were coming down toward us. Our men were a bit windy, but Hunter and I made them make a stand and fetch bombs. Hunter is a fine bomber, so he threw the bombs, while I carried on with a borrowed rifle and my revolver. We retired very slowly - the Boches were chucking their bombs. These bombs of theirs make an awful row, but don't do much damage unless you get too close to one. Unfortunately they had also got some of ours, which are of a different calibre. I was bringing up the rear as we retired, and was having quite a pretty little duel with the Hun Serg. Major who was leading their attack - he evidently wanted me as a prisoner, for every time we faced each other round a traverse he signed and shouted to me to put my hands up. Of course my only answer was revolver ammunition, it was not likely that I was going to put my hands up to a Boche. Well at last we got to a fair stock of bombs, so we made a halt and bombed steadily. Hunter stands 6 ft 4 in and throws bombs magnificently. This went on for about twenty minutes, and then we found that we were not being answered, so we decided to advance. First of the party came myself with my revolver - then came Hunter with bombs and one or two men. We went round two traverses then we came upon two Huns. The first was the Serg. Major - dead, the next was a young lad, he had been hit in the hand and had a nasty gash in his head. As this poor lad saw me he tried to collect himself but he was far too gone, I can see his bloodshot eyes now as he tried to raise his head - on the other side of the trench was a Boche officer, dead, As we advanced we found quite a number of dead, we had done better than anticipated - we made a rush and took six machine guns, one Minnen-werfer and coil of telephone wire. So we had managed to stop rather a large counter attack. The "D" Company Commander sent in a very good report to Battalion Headquarters about our work, which was encouraging. The Corporal and two men who backed us up have been recommended for the Distinguished Conduct Medal and the Military Medal. I have written but bald facts, of course there is much more but I must not tell just yet.The German Planes a…
The 1944 D.F.C. group of four awarded to Flight Lieutenant L. C. Ainsley, Royal Air Force, who ploughed on through heavy flak despite taking a total of four hits and successfully bombed the target: making it back to Britain he crash landed without any casualties and little damage to the aircraftDistinguished Flying Cross, G.VI.R., the reverse dated '1944'; 1939-45 Star (P/O L. C. Ainsley R.A.F.); France and Germany Star (F/O L. C. Ainsley No. 51. Sqd. R.A.F.; War Medal 1939-45 (F/O. L. C. Ainsley. D.F.C. R.AF.), all campaign awards privately in the same style, mounted court style as worn, sold together with a Buckingham Palace slip of issue named to the recipient and a related telegram, good very fine (4)D.F.C. London Gazette 31 October 1944, the original citation states:'This officer is a most competent pilot and a first-class captain of aircraft. One night in September 1944, he was detailed for an attack on a synthetic oil plant at Nordstefn. When nearing the target area the aircraft was hit by anti-aircraft fire and the starboard inner engine was rendered unserviceable. Shortly afterwards the aircraft was hit in the port aileron; making it difficult to steer correctly. In spite of this, Flying Officer Ainsley continued to the target and bombed it. On the turn for home the bomber was hit once more. The port engine was affected and the hydraulic system was put out of action. After crossing the-English coast the defective port engine became useless. Flight Lieutenant Ainsley thereupon headed for the nearest airfield where he made a safe landing with the undercarriage retracted. This officer set a fine example of skill, courage and tenacity.'Lawrence Cuthbert Ainsley enlisted with the Royal Air Force Volunteer Reserve on 19 June 1941 and was commissioned Pilot Officer with the General Branch on 21 April 1944. Initially posted to No. 41 base, Marston Moor, Yorkshire on 21 April he later joined No. 51 Squadron on 30 July. His first raid as a Captain of Aircraft occurred on 3 August 1944 in a Halifax III over Bors-de Cassan.Three further raids that month saw good results and Ainsley was present for an attack over Le Havre on 10 September. It was for the raid the next day, 11 September 1944, that he was awarded the D.F.C, the Squadron Record book provides details for that day stating:'This aircraft sustained flak damage over the target, causing on [SIC] engine to be feathered. On arriving over this country another engine had to be feathered, and the aircraft was landed safely away from base on two engines. No members of the crew were injured. The aircraft landed away from base.'The initial recommendation for the award expands upon this, stating:'On 11th September 1944 this officer was the captain of an aircraft detailed to attack the synthetic oil plant at Nordstorn. When about fifteen miles distant from the target and at 18,000 feet, his aircraft was hit by heavy flak which rendered the starboard inner engine unserviceable, but he continued one his course and shortly afterwards the aircraft was hit again, causing damage to the port aileron and making it difficult to handle. Flying Officer Ainsley still continued on his course, however, and although he was hit yet again and had lost height to 14,000 feet, he pressed home his attack and bombed the target. Then as he was turning away and was about to leave the defended area, the aircraft was hit by a fourth burst. This time the wireless operator was slightly wounded in the head, the hydraulics were hit and the port inner engine was destroyed.After clearing the Ruhr defences he set course for Woodbridge, but on crossing the English coast the port inner engine finally stopped and a crash landing had to be made at the nearest aerodrome. Without hydraulics to operate the undercarriage and flaps, he landed the aircraft without appreciable damage or any injury to the crew.Flying Officer Ainsley's devotion to duty in continuing to bomb the target in spite of serious damage to his aircraft and in the face of intense flak, and his skill in bringing his aircraft back and landing it without more serious consequences, deserves the highest praise and his courage and determination are an example to all.Flying Officer Ainsley had now carried out nine sorties against the enemy, and has proved himself to be a most competent pilot and a good captain and leader. He is recommended for the immediate award of the Distinguished Flying Cross.'The station Commander commanding R.A.F. Snaith added his own recommendation stating:'This officer undoubtedly showed courage and determination in pressing home his attack in the face of what appears to have been very accurate predicted flak, and a high degree of skill in bringing home his badly-damaged aircraft back to this country and landing it with so little damage and without injury to his crew.He also displayed great coolness and presence of mind, and proved himself to be an excellent operational captain. He is strongly recommended for the immediate award of the Distinguished Flying Cross.'This is back up by an exciting account in the Sunday Sun (Newcastle) on 29 October 1944 which states:'A young man called L. C. Ainsley born in Carlise in 1916, was working on a television research bench in America when the war began, but he was determined not to miss it. So he "jumped" an oil tanker and worked his way to England. To-day he is Flying Officer Ainsley and has just gained the immediate award of the D.F.C. for fine work during the bombing of the oil works at Nordstern. His Halifax was thrice hit before reaching the target - but it got there. One more it was hit after the bomb load had gone - but it got home with a crash-landing near a drome. Now he thinks he will stay on this side of the Atlantic and make the R.A.F. a career. He has married a Scots Girl.'Ainsley was advanced Flying Officer on 21 October 1944 and continued to fly, seeing a total of seventeen successful sorties. Transferred to R.A.F. Tangmere on 15 May 1945 he was posted to the Administrative and Special Duties Branch on 26 April 1945 and then transferred to Andrews Field on 27 July.Several more transfers occurred to sites such as R.A.F. West Malling on 5 September, Castle Camps on 27 September and R.A.F. Duxford on 10 December. However he was to leave the R.A.F. under a cloud, being dismissed by sentence of a Court Marshal on 6 August 1946.…
The stretcher-bearer's D.C.M., 'Great War' M.M. group of four awarded to Corporal W. J. Barltrop, 17th (British Empire League) Battalion, King's Royal Rifle CorpsDistinguished Conduct Medal, G.V.R. (C-3553 L.Cpl W. J. Barltropp. 17/K.R.R.C.); Military Medal, G.V.R. (C-3553 L.Cpl W. J. Barltrop. 17/K.R.R.C.); British War and Victory Medals (C-3553 Cpl. W. J. Barltrop. K.R.Rif.C.), some light edge wear, minor contact marks, overall very fine (4)D.C.M. London Gazette 22 October 1917, the original citation states:'For conspicuous gallantry and devotion to duty as stretcher bearer. He worked untiringly for six days, dressing the wounded under fire with admirable skill and disregard of personal danger. During this time he carried a wounded man, who was in need of immediate medical treatment, over ground which was swept by enemy snipers; they had already that day accounted for four runners who were using the same road. No praise can be too great for his courage and devotion.'M.M. London Gazette 6 January 1917.William James Barltrop, sometimes spelled Barltropp, was born near Hemel Hempstead, Hertfordshire around 1886. He appears on the 1901 census living at Henham Hall Cottages, near Stansted, Saffron Walden. Enlisting with the 17th (British Empire League) Battalion Barltrop entered the war in France with them at some stage after 1916.The Battalion entered the war in April 1916 and saw action during the Somme Offensive starting at Ancre in September before moving to support the attack on the Schwaben Redoubt in October. Given the date of Gazette for Barltrop's M.M. it is quite likely that his medal was related to these actions.The 17th Battalion saw out a gruelling Christmas and New Year in the Ypres Salient suffering a constant attritional stream of losses. They were back in the action proper at the start of the Third Battle of Ypres at Pilckem Ridge and saw continual fighting through July, August and into September. It was very likely during the early engagements of that Offensive that Barltrop won his D.C.M.The Regiment was seriously mauled during the German Spring Offensive of early 1918 and as such they were amalgamated into a composite Brigade. After the Offensive was halted they went into the reserve as a training cadre. Barltrop appears to have taken his pension from April 1919, his death was registered in 1925; sold together with copied research.…
The Naval General Service Medal awarded to Rear-Admiral E. R. P. Mainwaring, who saw a remarkable forty-two years of active service and commanded the boats during the capture of the American letter-of-marque Rapid in 1814Naval General Service 1793-1840, 1 clasp, Egypt (E. R. Mainwaring.), note absence of third initial, good very fineEdward Reeves Philip Mainwaring was born on 16 June 1788 at Prince Edward Island, Canada. Scion of a great 'fighting' family of Whitmore, Staffordshire and with lineage stretching back to the Norman Conquest, his father fought during the American War of Independence and all four brothers also entered either the Army or Royal Navy - one, Benjamin, was an officer aboard 'The Fighting Temeraire' at Trafalgar and another, Frederick, fought at Waterloo as a Lieutenant in the 51st Regiment of Foot.Young Edward entered the Navy in the summer of 1799 as a First-Class Volunteer and was appointed to the 44-gun H.M.S. Roebuck which acted as a troopship between March and September 1801 for British operations during the Egyptian campaign. In November 1801 he was appointed Midshipman in the 64-gun H.M.S. Haarlem and, as was usual for the time, continued to receive appointments to other vessels when required. He was advanced to Acting-Lieutenant in 1806 aboard the 18-gun sloop H.M.S. Espoir but shortly afterward was promoted Lieutenant (11 June 1807) and removed to the 74-gun H.M.S. Plantagenet, with which vessel he saw out the rest of the Napoleonic Wars.It was with this ship that Mainwaring appears to have experienced the most exciting days of his active service. After a deployment to the Baltic Plantagenet and her crew were next assigned to the North American and West India stations. Consequently seeing much action during the War of 1812, Mainwaring must have been aboard in July 1813 when U.S. Navy Sailing Master Elijah Mix tried to destroy Plantagenet with torpedoes designed by inventor and engineer Robert Fulton. Mix made the attempt no less than seven times; the first six all missed, and the seventh prematurely exploded. The 'Yankey Torpedo' was a known threat to officers and men of the Royal Navy, and one wonders what Mainwaring thought about being on the receiving end of such an 'ungentlemanly' way of warfare.Returning to more traditional ways of engaging with the enemy, in 1814 Plantagenet was pursuing the American latter-of-marque Rapid when both vessels were becalmed when the wind died away. Mainwaring was ordered to take command of the ship's boats and, after rowing for an astonishing 11 hours, came up with the Rapid, boarded and captured her notwithstanding a spirited defence by her crew of 40 men. For this action, Mainwaring was publicly thanked by the Commander-in-Chief of the North American Station, Admiral Sir John Borlase Warren.Despite the vast reductions in manpower and ships in the aftermath of the conflict, after a mercifully short period on half-pay (1815-18) Mainwaring was fortunate to be employed at sea once again and for the following eight years served aboard the 74-gun Ramillies and the 84-gun Ganges; in the latter vessel on the West India and Brazilian stations as well as at home. Promoted Commander on 27 May 1826, perhaps a desire to somewhat settle-down led to both an appointment with the Coast Guard service and his marriage to Miss Eliza Hill, daughter of the Reverend Hill, Rector of Snailwell in Cambridgeshire. He was employed by the Coast Guard until 1835 and four years later was given command of the 18-gun sloop H.M.S. Electra on the South America Station, returning home in 1841 on promotion to Captain. Slowly but steadily rising up the seniority list to be promoted Rear-Admiral (Retired) on 12 April 1862, Admiral Mainwaring died at Brighton on 5 October 1865 at the age of 77, with his death being noted in many local newspapers and journals - all of which specifically state that he was actively employed for more than 40 years; an impressive feat indeed during the age of sail and many years of peace in Europe.…
The '1916 Trench Raid' D.C.M. awarded to Sergeant H. P. Evans, 19th Battalion, Australian Infantry, who was killed in action during the final days of the Somme OffensiveDistinguished Conduct Medal, G.V.R. (1890 L.Cpl. H. P. Evans. 19/Aust:Inf:), nearly extremely fineD.C.M. London Gazette 22 September 1916, the original citation states:'For conspicuous gallantry during a successful raid on the enemy's trenches. He carried in the body of a sergeant, who had been killed, 200 yards under intense shellfire. On another occasion he shot the leader of an enemy patrol whilst reconnoitring.'Hamblett Poole Evans was born at Coldfield, Warwickshire in 1889, the son of George and Kate Evans of Silverdale, Manor Road, Sutton Coldfield. Emigrating to Australia he was working as a storekeeper when the Great War began and joined the Australian Imperial Force in New South Wales, being posted to the 19th Battalion.This unit was posted to Gallipoli, arriving at Anzac Cove just after the initial landings they saw action at the attack on Hill 60. Evans was not to remain with the unit for the duration of their time in Gallipoli, being evacuated with gonorrhoea on 13 November. Almost immediately upon his recovery he caught malaria on Lemnos which incapacitated him until after the evacuation of the peninsula.He joined the British Expeditionary Force Evans and the rest of the Battalion went into the trenches in the Armentières area. Around this time his service papers record:'Complimented by Lt Gen W. R. Birdwood K.C.S.I., K.C.M.G., C.I.E., D.S.O., in Army Corps Orders dated 26.6.16. for gallant action on the night of 20/21st June 1916.'A week after the action he was commended for, on the night of 25-26 June he took part in a trench raid, it seems to have been for this action that the award of the D.C.M. was made. Caught in a shell blast in August, Evans was evacuated to Britain with shrapnel wounds and a sprained ankle.Rejoining his unit on 3 November he was with them for the capture of Gird trench on 14 November 1916. Evans was killed in action during the attack and is commemorated upon the Villers-Bretonneux Memorial.…
An 'Arnhem P.O.W.' group of five awarded to Corporal R. S. Telford, 7th Battalion, King's Own Scottish Borderers, who went 'in the bag' on 23 September during a fierce tank attack on the Battalion's perimeter1939-45 Star; France and Germany Star; Defence and War Medals 1939-45; Cadet Forces, E.II.R. (WO. R. S. Telford. A.T.C.), sold together with the recipient's dog tags and soldier's release book, light pitting and contact marks, very fine (5)Robert Smith Telford was born on 13 June 1919, a native of Dumfriesshire and enlisted on 1 September 1939 with the King's Own Scottish Borderers. Joining the 7th (Galloway) Battalion he was with them in Scotland during the Fall of France, indeed the Battalion was not to leave Britain for some time. They transferred to the 1st Air Landing Brigade in 1943 and continued to train with them until the D-Day Landings.7th Battalion took off on 17 September 1944 for Operation Market Garden, landing in the Ede area in 1944 and initially all went well. The next day however they came under attack by several parties of German troops with armoured vehicles in support, a situation which would become increasingly familiar over the next week of fighting.Moving off they fought a sharp action at Johanna Hoeve farm but managed to repel a German attack and continue on towards Arnhem. Arriving at Oosterbeek, some 5 kilometeres west of Arnhem on 19 September they dug in there to assume their corner of the perimeter. The enemy started to probe their lines not long later, and by 09:00 on 20 September they had established the Battalion's positions allowing the battle to begin in earnest. Some of the ferocity of the fighting can be ascertained from the war diary which notes the first armoured 'kill' made by the unit:'The first "kill" was an armoured car which was blown up and set on fire by the atk gun covering the NORTH face. Later another atk gun under Lt HANNAH, and escorted by a Pl of B Coy, went out to watch the rd leading SOUTH from the rd and rly crossing at 699791. Soon after it was in posn a TIGER tk, towing a flame-throwing apparatus, appeared and a spirited action took place. As a result of the courageous behaviour of our atk gun crew, and of Cpl WATSON and Pte McWHIRTER in particular, the TIGER tk was completely knocked out and the crew killed.'Through that day and the next, 7th Battalion halted the enemy advance, unable to withdraw due to constant pressure and concern over losing their limited equipment in the dark. A break in the attacks on 22 September allowed them the chance to reform and prepare their positions for another attack, however they could not have been prepared for the forces ranged against them.A heavy barrage opened the day and at around 11:00 'B' Company came under heavy attack by a force of tanks with infantry and artillery support. Their anti-tank gun was knocked out, forcing them back from a line of buildings, however they gamely held on to their slit trenches and bunkers, fighting for every yard. Their partial withdrawal allowed the German infantry to push onto the flank of 'C' company who also came under attack from Armoured cars to their front.Soon the action became an attempt by the Germans to consolidate a piece of their hard won gains in the face of heavy fire and counter-attacks by the Battalion. They were able to prepare machine gun positions in the wood between 'B' and 'C' companies, thus keeping that gap open and completing their objective.The only option was a counter-attack which was carried out by 'C' Company, who despite several losses managed to retake the wood and capture a number of the enemy. The line re-established they managed to hold off further attacks for the rest of the day, taking a tally of German tanks, damaged or destroyed in the process. It was noted in the war diary that the Regimental Aid Post was full to bursting as the Medical Aid Post had fallen into enemy hands, suggesting that some areas of the perimeter were still occupied by the enemy.Telford is listed as being taken prisoner of war during the days fighting, it is likely he was a victim of the morning offensive which almost saw the line break. Taken to Stalag 11B at Fallingbostel he remained there until being repatriated at the end of the war. Upon his return to the British Army he was posted to a Holding Regiment, Royal Artillery but saw no service with them instead being demobilised on 11 April 1946. Later joining the Cadet Forces he was awarded the Cadet Forces medal with them. Telford died in Dumfries on 8 December 1898 and is buried at Lockerbie; sold together with copied research, a set of original dog tags and an original soldier's release book named to the recipient.…
A good 'Air Gunner's' D.F.M. group of five awarded to Flight Sergeant A. Massey, No. 51 Squadron, Royal Air Force, who served in multiple air combats, certainly downing an Me109Distinguished Flying Medal, G.VI.R. (649458 F/Sgt. A. Massey. R.A.F.); 1939-45 Star; Air Crew Europe Star; Defence and War Medals 1939-45, light contact marks, very fine (5)D.F.M. London Gazette 13 October 1944, the original recommendation states:'Flight Sergeant Massey has completed 29 sorties against the enemy, 21 of these against heavily defended targets in Germany. On several occasions, his aircraft has suffered damage and at all times his coolness and courage in the face of the enemy fire has been an inspiration to his crew. He has had several combats with enemy fighters and on one occasion destroyed an ME109. His devotion to duty at all times set a good example to his fellow gunners and as a crew member, he inspire[d] great confidence. This NCO is recommended for the award of the DFM.'Allan Massey was serving with No. 51 Squadron in 1943, operating out of R.A.F. Snaith as part of No. 4 Group. He was with them on 27 August when his aircraft was attacked by a JU88, they managed to lose him in the clouds but were hit by flak on the return journey. Another dramatic incident occurred in early August 1943 when the rear turret gunner collapsed and had to be returned to base for medical treatment.The mission for which Norcross was awarded his D.F.C. occurred on 30 August, in an attack over Muchen-Gladback. The Squadron Operations Book adds further details:'10 miles NNE Antwerp. Mid Upper gunner saw twin engine aircraft on port side coming in towards Halifax. Mid Upper Gunner fired about 25 rounds, and enemy aircraft dived to starboard and was lost to sight.'His station commander added his recommendation for the award of the D.F.M., stating:'Flight Sergeant Massey is a thoroughly competent and reliable Air Gunner and by his skill and determination has contributed to the success of his crew and to the safe completion of an operational tour. His ability and spirit have been a fine example to his unit. Strongly recommended for the award of the D.F.M.'…
China 1842 (E. Pitman, Lieutenant, 55th Regiment Foot.), fitted with replacement silver clip and swivel suspension, pitting, very fineEdmund Pitman was born circa 1820, the son of Major Pitman of Dunchideock House, Devon. Young Pitman joined the 55th as an Ensign in January 1837, he served as a Lieutenant in the First Opium War with the 55th (Westmoreland) Regiment of Foot, who saw a great deal of action in that campaign. Deployed to China in 1841, they participated in the Battle of Amoy in August of that year and were the first to land from the boats at the disembarkation and subsequent capture of Chusan that October. During this action, the 55th assaulted Guards Hill under heavy fire but successfully took the position before going on to capture the heights above Tinghai; they then planted their Regimental Colours on the walls of the city.On 10 October the regiment participated in the Battle of Chinhai, forming the garrison of that city until the following year when they played yet another active part in the battles of Chapu and Chinkiang - remaining in garrison of the latter until the Treaty of Nanking was signed on 29 August 1842. The 55th subsequently received the battle honour "China" and a dragon badge was added to their Regimental Colour.Pitman was presented to Queen Victoria by Colonel Sir J. H. Schoedde in May 1845 and was promoted Captain. Latterly serving as Adjutant of the 1st Devon Militia, he died at Heavitree, Exeter in January 1882.…
Military General Service 1793-1814, 1 clasp, Java (Samuel Whittle, 22nd Light Dragoons.), traces of brooch mounting at 3 and 9 o'clock respectively, suspension sometime re-affixed, some edge bruising and contact marks, otherwise very fineWhittle is one of only 54 members of the cavalry with entitlement to a clasp for Java.Samuel Whittle was born in Whitley, Chester circa 1778 and made his living as a hatter prior to his enlistment with the 22nd Regiment of Light Dragoons on 1 July 1795 upon reaching eighteen years of age. Whittle was to embark on what would be a twenty-four-year career with the Colours, twenty-one of which were to be spent serving abroad in the East Indies.The 22nd Light Dragoons were renumbered from the 25th Dragoons in 1794, which had been raised by Francis Edward Gwyn that same year for service in India. Whittle, therefore, joined the Regiment whilst it was still in its infancy and was likely first embarked to India with the rest of his unit to serve in the Anglo-Mysore War in 1799. Whittle would remain in the region for the next two decades. The conflict in Mysore saw the 22nd Light Dragoons fight with distinction at the Battle of Seringapatam, which was awarded to them as a battle honour.During the Napoleonic Wars, Whittle and his Regiment took an active role in the British effort to seize Java from Franco-Dutch forces in 1811. They landed on 4 August and the next day a small number escorted Colonel Robert Gillespie to the capital of Batavia. They reached the undefended city on 8 August, which immediately surrendered to Gillespie and his men. They next advanced on Dutch General Janssens stronghold at Weltervreeden, which fell to a British attack on 10 August. The British sustained under 100 losses while the enemy lost over 300 men. The nature of the island made the deployment of cavalry difficult, however after the action at Weltervreeden the 22nd were utilised in their traditional role of pursuing the retreating enemy. Some of the Regiment may have taken part in the fighting dismounted, as Gillespie's Brigade Orders refer to:'I have also to thank Captain Gall of the Body-guard, Lieutenant Dudley of the dismounted dragoons twenty-second regiment, and Captains Smithwayte and M'Craith of the Madras pioneers, for their support in the affair.'Lieutenant Dudley's Dragoons also participated in the siege of Fort Cornelis which took place later that month. The column was guided into position by a Franco-Dutch deserter who rode at their head with Serjeant Smith of the 22nd, capturing two enemy redoubts in the surprise attack after a fierce battle, at which the critical moment Gillespie led the mounted detachment of the 22nd after the fleeing enemy. The Batavians rallied several more times prolonging the conflict, however in the end most of the force was cut off and the British seized the fort on 25 August. The British sustained 630 casualties, with the 22nd suffering 6 dead and 17 wounded. The wounded included the commander of the dismounted detachment, Lieutenant Dudley, who was again 'mentioned' although this time by the Adjutant General. The Battle of Cornelis ended effective resistance in Java, though the stubborn resistance of General Janssens carried on into September.The 22nd remained in Java until 1813, after which Muster Lists indicate that they served in Bangalore, India. British occupation of the island came to an end in 1814 when Java was returned to the newly independent Netherlands. Whittle was promoted Corporal in India on 22 February 1814 and served in this capacity with John Floyd Patterson's troop. The Regiment remained there and as such did not fight at the Battle of Waterloo in 1815.Whittle was at some stage advanced Serjeant, and served as such at the Battle of Maheidpoor in Captain Vernon's troop on 21 December 1817. This battle saw a decisive British victory over the Marathas, resulting in the conclusion of the Anglo-Maratha War and the cession of much territory to the British, which were incorporated into the British Raj. It was just a few years after the engagement at Maheidpoor that Whittle's time in the service finally came to an end. He was discharged in India in consequence of 'being worn out by length of service & unable to ride' on 25 August 1819. While this poor state of health is certainly understandable given his twenty years in the harsh Indian climate, one wonders if his discharge might have been influenced by his Regiment being disbanded the following year.Whittle is further entitled to an Army of India 1799-1824 Medal with a clasp for Maheidpoor, being one of only 167 Europeans with entitlement to the clasp, 28 of which were awarded to the 22nd Light Dragoons; sold together with copied research including medal rolls.… 25001 SALEROOM NOTICE:Lot is NOT subject to 5% Import Tax.
The 'St. Pancras bombing 1941' B.E.M. awarded to Constable H. J. Smith, Police War Reserve, 'N' Division, Metropolitan Police who, whilst off duty, saw a women trapped in her home by a parachute mineFinding a ladder he climbed the crumbling, bomb damaged building, dug her free and pulled her to safety, all while the bombs continued around him, his original recommendation was for the George Medal, later downgradedBritish Empire Medal, Civil Division, G.VI.R. (Henry John Smith), officially engraved naming on a pre-prepared background, light edge wear, very fineB.E.M. London Gazette 12 September 1941, the original citation states:'A bomb damaged a building, the remains of which were liable to collapse. War Reserve Constable Smith obtained a ladder, climbed to the top of it and then hauled himself on to a balcony which went round to the first floor. He climbed through a window and entered a room where he found a woman buried up to the neck in rubble. He began to dig with his hands although debris was falling and further bombs were dropped in the neighbourhood. Smith eventually released the victim and carried her to safety.'Henry John Smith worked as a packer in civilian life and was living at 41 Goldington Buildings, St. Pancras during the Second World War. He volunteered for the Police War Reserve and was posted to 'N' Division, Metropolitan Police. The original recommendation for his award was for the George Medal however it was downgraded to the B.E.M., the text goes into further detail on the events of 17 April 1941:'On 17th April 1941 at about 3.15 a.m. a parachute mine fell in Pancras Square, Platt Street, N.W.1., causing widespread devastation to the surrounding property including a very large block of flats and the "Star" P.H. at the corner of Platt Street and Goldington Street.War Reserve Smith, who was off duty but lived in the vicinity had returned from assisting at another incident at St. Pancras Hospital when he saw a parachute mine descending in the vicinity of Somers Town Police Station. He immediately went towards Pancras Square and while on his way the mine exploded. On arriving at the scene he rendered assistance, in the course of which he rescued a pregnant woman, and then heard cries for help coming from the first floor of the public house.This building appeared to be in imminent danger of collapse and part of it had to be pulled down next day, but War Reserve obtained a ladder (which was too short) climbed to the top of it and then hauled himself on to a balcony which went round the first floor. He climbed through a window and entered a room where he found a woman buried up to the neck in rubble and debris. He began to extricate the woman with his hands although pieces of ceilings and brickwork were falling and further bombs were still coming down in the neighbourhood.The woman was eventually released and carried to the window. War Reserve Smith then shouted to another police officer to fetch a longer ladder and when this arrived he put the woman over his shoulder and descended to the ground. She had by this time fainted.With the assistance of the woman's brother-in-law he took her to a Rest Centre and then returned to the scene of the incident and rendered what further assistance he could until 5.15 a.m. when he returned home, cleaned himself and reported for duty at 5.45 a.m. at Somers Town Police Station.Although War Reserve Smith was due to parade for duty at 5.45 a.m. the same morning he voluntarily rendered assistance at various incidents during the night. He attended a major incident at St. Pancras Hospital and then generally assisted at Pancras Square, in the course of which he rescued the two women. It is likely that had it not been for the efforts of this War Reserve the second women would have been buried by debris.The conduct of War Reserve Smith, who was off duty, was meritorious and his conduct was of a very high order.The acting Superintendent of the Division recommends War Reserve Smith for an award or mention in the London Gazette. The Deputy Assistant Commissioner of the District considers his conduct worthy of high award and recommends the award of the George Medal.'Whilst impressive this recommendation does little to underline the danger of the situation and can be better outlined by the testimony of the witnesses, firstly the victim of the bomb, Mrs. Constance E Keevil, who states:'My house partially collapsed, and as I attempted to leave my office the door collapsed on me, pinning me in the corner with the door, by this time the ceiling and walls were collapsing on me, burying me in the debris up to my shoulders. I was completely helpless, and shouted for help; this was answered by a man's voice, telling me to wait; shortly afterwards a policeman entered my office through the balcony window, he started to clear the debris off me with his hands, repeatedly telling me to keep calm. All the time he was doing this masonry was falling in patches and was dangerous to us both. He eventually cleared me of the debris, took me to the window and shouted for someone to bring a longer ladder, still doing his best to keep me calm, which I might say was a great effort on his part. The raid was still very heavy; the next I remember was being thrown over the P.C.'s shoulder and carried down the ladder when I completely collapsed.'P.C. Richardson adds his verdict:'The air raid was still in progress and of a severe character; the public house was in a very bad condition and liable to collapse further.In my opinion The War Reserve acted with great promptitude and courage, and at great personal danger considering all the circumstances of the night.'Sold together with copied research.…
The 2-clasp Naval General Service Medal awarded to Admiral Alexander Montgomerie, Royal Navy, who served at sea for almost twenty years and participated in a number of fiercly-fought actions, not least at Barque island; the subsequent capture of Guadeloupe; and at Rugen island where he successfully defended a fort against French infantry assaultsNaval General Service 1793-1840, 2 clasps, Anse La Barque 18 Decr 1809, Guadaloupe (Alexr. Montgomerie, Lieut. R.N.), good very fineProvenance:Sotheby's, March 1995.Colin Message Collection, August 1999.Jason Pilalas Collection, July 2024.Alexander Montgomerie, of an old Scottish family, was born at Dreghorn, Ayrshire, Scotland on 30 July 1790. Joining the Royal Navy at the tender age of 12 on 27 June 1802, he was initially appointed a First-Class Volunteer aboard the 16-gun sloop H.M.S. Hazard, with which he saw brief service in the English Channel before spending the next six years with both the 44-gun frigate H.M.S. Argo and the 74-gun H.M.S. Tigre, as a member of their Midshipman's berth. With Argo (under the command of Captain Benjamin Hallowell) young Montgomerie saw his first taste of action, as this vessel participated in the captures of St. Lucia and Tobago - the former earned Hallowell and his men a very favourable 'Mention', with Admiral Hood stating: 'To Captain Hallowell's Merit it is impossible for me to give additional Encomium, as it is so generally known; but I must beg Leave to say, on this expedition, his Activity could not be exceeded; and by his friendly Advice I have obtained the most effectual Aid to this Service, for which he has been a Volunteer, and, after the final Disembarkation, proceeded on with the Seamen to co-operate with the Army.' (London Gazette, 26 July 1803, refers).When Hallowell was appointed to command the Tigre, Montgomerie followed him and this ship was part of Admiral Lord Nelson's fleet in the great hunt for the combined Franco-Spanish fleet prior to the Battle of Trafalgar on 21 October 1805. Tigre, unfortunately, missed the battle due to being away at Gibraltar to take on water and escort convoys, but subsequently participated in the operations off Egypt in 1807: Montgomerie must have been aboard when Tigre captured two Ottoman frigates (the Uri Bahar and Uri Nasard) and his subsequent biography states he was then employed with 'much boat service' on Lake Mareotis - scene of British landings against French, Ottoman, and Albanian troops.In September 1809, Midshipman Montgomerie passed his Lieutenant's examination and was thence sent (though still as Midshipman) to the 36-gun frigate H.M.S. Orpheus, before shortly afterwards removing to the 74-gun H.M.S. Sceptre - the ship with which he was to earn the clasps to his Medal. Sceptre, commanded by Captain Samuel James Ballard, was part of a force ordered to capture the French-held island of Guadeloupe. On 18 December 1809, a British squadron (including Sceptre) attacked two French ships (the Loire and Seine, variously described as 'frigates' or 'flutes') anchored at Anse a la Barque and protected by batteries of artillery ashore. Notwithstanding a spirited defence, in fairly short order both French vessels had been dismasted and surrendered - though they were subsequently abandoned, caught fire, and blew up. The attack was under the overall command of Captain Hugh Cameron of H.M.S. Hazard, and after destroying the Loire and Seine the British force next landed ashore to silence the batteries: this objective was also achieved but in the moment of victory Cameron was killed, one report stating that after personally hauling down the French tricolour he wrapped it around his body before being accidentally shot by a British sailor who mistook him for the enemy. It seems likely that Montgomerie played a very active part in this action, as the very next day he was appointed Acting Lieutenant of H.M.S. Freija/Freya, which was confirmed by official commission on 4 May 1810, and during the intervening time also appears to have been equally active in the ships' boats in minor actions against further French shore batteries around Guadeloupe.Returning home, after three months in command of H.M.S. Magnanime on 28 January 1811 he was appointed Lieutenant aboard the 32-gun frigate H.M.S. Aquilon, with which vessel he served until 1814, concluding his time aboard her as First Lieutenant. This period of his career also saw much active service - but rather than the tropical Caribbean, this time in the distinctly cooler North Sea and Baltic in the supression of enemy trade and coastal traffic, and the escorting of British and allied convoys. Though little further information appears immediately available, his service biography states that: 'When in the Baltic in 1812, and engaged with the boats under his orders in an attempt to bring some vessels off from the island of Rugen, he greatly distinguished himself by his conduct in capturing a temporary fort occupied by a superior number of troops, whom, on their being reinforced and endeavouring to recover their loss, he several times repulsed.' (A Naval Biographical Dictionary - Montgomerie, Alexander, W.R. O'Byrne, p.774, refers).Promoted Commander on 7 June 1814 on his return from the South America station, despite theoretical appointment to H.M.S. Racoon she was off the coast of Brazil and he never joined her. With the conclusion of the Napoleonic Wars Montgomerie had to wait until 21 March 1818 for his next command - the 18-gun brig-sloop H.M.S. Confiance, which position he held for two years until moving in July 1820 to the 26-gun H.M.S. Sapphire as Acting-Captain. This was a fortuitous change as, two years later, Confiance was wrecked off Ireland with the loss of the entire crew. Returning home in September 1821, he does not appear to have received another seagoing appointment but nevertheless remained on the Active List until his official (and well-earned) retirement on 1 October 1856.By virtue of longevity, Montgomerie moved slowly up the seniority list; promoted Rear-Admiral in 1852, then Vice-Admiral in 1857, he reached the rank of Admiral on 27 April 1863. Admiral Alexander Montgomerie appears to have remained a bachelor throughout his life and died in January 1864 at Skelmorlie, Ayrshire, not far from where he was born 73 years earlier.Sold together with a small quantity of copied research.…
A fine 1953 A.F.C. and wartime pilot's group of seven awarded to Squadron Leader L. K. Grzybowski, Royal Air Force, late Polish Air ForceA a Pilot in No. 131 Polish Fighter Squadron, he quickly saw action in September 1939 when he was credited with the destruction of two German aircraft, actions for which he was later awarded the Virtuti Militari, 5th ClassSubsequently taken P.O.W. by the Russians, he was released for service in the Polish Army in Russia and the Middle East, prior to reaching the U.K. and undertaking a protracted tour of 56 sorties of a 'Ramrod' nature in Mustangs of No. 306 Squadron in 1944-45, gallant work that won him the Cross of Valour and BarAir Force Cross, E.II.R., the reverse officially dated '1953'; 1939-45 Star; Africa Star; France and Germany Star; War Medal 1939-45; Poland, Virtuti Militari, 5th Class, GR Tech type as issued in late 1944-45; Poland, Cross of Valour, with Bar, mounted as worn, together with his Polish Pilot's Badge, by J. R. Gaunt, embroidered R.A.F. uniform wings and Flying Log Books, generally very fine or better (9)A.F.C. London Gazette 1 January 1953.King's Commendation for Valuable Service in the Air London Gazette 1 January 1952.Leszek Kazimierz Grzybowski was born in Dabrowa Gornicza, Kielce, Poland on 20 December 1915 and entered the Polish Air Force College in August 1935.Duly qualified as a pilot, he joined No. 131 Polish (Fighter) Squadron at Poznan in October 1938 and was likewise employed at the outbreak of hostilities. As cited, he was quickly credited with the destruction of two German aircraft, namely a share in a He111 on 3 September and a Me110 on 9 September. He may also have contributed to the destruction of a Ju86. More certain, however, is the fact he was taken P.O.W. by the advancing Russian Army in the same month and remained behind wire until April 1942, when he was released for service in the Polish Army in Russia and the Middle East.Having then reached the U.K. in February 1943, he undertook a succession of training courses and joined No. 306 (Polish) Squadron in August 1944. Here, then the commencement of a protracted operational tour in which he flew 56 sorties in the unit's Mustangs over Austria, Belgium, Germany and Holland, the majority being of a 'Ramrod' nature and including numerous outings to the Ruhr and one to Arnhem in support of 'Market Garden' in September 1944. But he also flew several 'anti-diver' (V-weapon) sorties off the English coast in March 1945, And his final sortie, flown on 25 April 1945, was a trip to the Nazi playground of Berchtesgaden, home to Hitler's 'Eagle's Nest'.According to records held by the Sikorski Museum, he was awarded the Polish Cross of Valour in April 1945, a Bar in August 1945, and the Virtuti Militari, 5th Class on 25 July 1945, 'for actions in the Polish campaign in 1939, when serving in 131 Fighter Squadron'. He also appears to have been entitled to the Polish Air Medal and 2 Bars.Post-warGrzybowski retained his commission in the R.A.F. after the war and remained on the strength of 306 Squadron until January 1947, when he was posted to the Polish Re-settlement Corps in Framlingham, Suffolk. Several months later he joined a communications unit at R.A.F. Tangmere, about which time he was married to Joan Fleming at Carshalton Beeches, Surrey.Two further stints with the Re-settlement Corps having followed, he joined an instructor's course at South Cerney in early 1949, thereby shaping the future of his R.A.F. career and adding to his laurels the A.F.C. and King's Commendation for Valuable Service in the Air for services in the Central Flying School 'Refresher Squadron' at R.A.F. South Cerney.He continued to fly after his retirement from the R.A.F. in December 1970 and died in Tadcaster, Yorkshire in August 1992.Sold with a quantity of original documentation and photographs, comprising:i)The recipient's R.A.F. Pilot's Flying Log Books (4), covering the periods September 1943 to December 1950, January 1951 to December 1957, January 1958 to November 1970, and June 1971 to January1976, the first with ink endorsement regarding missing Polish Air Force log book and some 500 hours.ii)A small selection of career photographs, including a studio portrait in uniform and a card-mounted group photograph of 'B Flight, No. 4 Squadron' in June 1943, with multiple signatures to reverse.iii)A large selection of wartime and later correspondence, mainly in Polish, and including Red Cross communications from a Polish P.O.W., exchanges with fellow pilots in the U.K., and a reference from a former C.O. at R.A.F. Coltishall, dated 20 May 1947.…
'My dear dear Dad, I am writing to you not Mum, so that you may break it more gently to her. Poor little Mole is dead. Oh it is too awful just Nick and then my favourite brother. I saw the whole thing at the time & had a terrible feeling that it was one of our machines and not a Hun and that if that was the case it would be him. He died protecting me.They went over to attack these Huns as they came up to the line and fought for about five minutes and then one machine broke away on fire. It was the most glorious fight for life ever put up. All who saw it say the same thing, what a wonderful Pilot he must have been.He was seen to be his by his Flight Commander before the fire started and then with the machine under control brought to down from 7,000ft to 100ft in a series of side slips so keeping the flames off himself, when it then broke up.I can't give you any hope and I think perhaps it was better for him to have been killed at the finish. I have kept nothing from you and I will leave it to you to say what you feel best to Mum.He was wonderful and loved by all. It nearly kills me to write this, but we must all try and bear up.Your broken hearted son, Lio.'Captain Woodhouse writes home to his father on the death of his brother, Lieutenant M. G. 'Mole' WoodhouseThe campaign group of three awarded to Flight Sub-Lieutenant M. G. Woodhouse, Royal Naval Air Service, who was tragically killed in action on 9 August 1917, by 37-kill Ace Leutnant Julius Buckler of Jasta 17; he had gone in to combat in order that he might save his elder brother who was also in the same aerial combatBritish War and Victory Medals (Flt. S. Lt., M. G. Woodhouse, R.N.A.S.); Great War Bronze Memorial Plaque (Mosley Gordon Woodhouse); Great War Memorial Scroll in the name of ‘Flight Sub-Lt. Mosley Gordon Woodhouse, R.N.', the V.M. with officially re-impressed naming, good very fine (3)Provenance:Glendining's, March 1990.Mosley Gordon Woodhouse - or Mole/Moley to his friends and comrades - was born on 26 October 1898. The family at that time lived at ‘Tofts’, Little Baddow, Essex.Having joined the Royal Naval Air Service as a Probationary Flying Officer at Dover 5 November 1916, he was slightly injured on 2 March 1917 when in a forced landing after engine failure on Avro 504 at R.N.A.S. Redcar. Posted to No. 3 (Naval) Squadron flying Sopwith Pups, he was advanced Flight Sub-Lieutenant on 10 June 1917 and crashed on 20 June 1917. Woodhouse joined No. 12 Squadron on 25 June 1917 at Dunkirk and sent to the front with No. 9 Squadron on 30 June 1917, equipped with Sopwith Pups, and Triplanes but by 12 July were exchanged for Sopwith Camels. On 9 August, while out on Patrol with Flight Commander Simpson and Flight Sub-Lieutenant Mellersh, took part in a fight with Albatros Scouts which were attacking an R.E.8., which turned out to be Piloted by his brother. His machine was shot down in flames by Vzfw. J. Buckler of Jasta 17, as his 12 'kill' of an eventual 35.Christopher Courtney wrote to his father on 14 August 1917:'Dear Arthur,I feel I must write to you and give my most sincere and heartfelt sympathy in the loss of your boy. I was terribly shocked to hear of it, but it was some small consolation to know that he went out gallantly fighting.I wonder if your eldest son has told you that he was killed in an endeavour to protect his brother's machine from attack?He probably did not know it but there was an artillery machine being attacked and so he at once dived in order to chase off the enemy; unfortunately he was caught by several enemy scouts and shot down but he certainly succeeded in drawing them off the artillery machine in which, it afterwards turned out, was his brother.I think it was a most gallant death. I went to his funeral, a simple and straightforward one; he is buried under the shadow of the sand-dunes in a quiet and secluded spot.I feel very guilty in not having answered your letter; I am afraid I am a bad correspondent at the best of times; but I had had it in mind for some days to write and tell you that he was in a good squadron and getting on well; his Squadron Commander spoke most highly of him.'Sold together with the original - highly poignant - letter from Lio Woodhouse to his father, on the loss of 'Mole', besides forwarding letter for his campaign Medals, besides photographs and a quantity of copied research, including his Flying Log Book.…
The superb 'mine-clearance 1943' M.M. group of seven awarded to Lance-Sergeant W. F. T. Beet, Royal Engineers, who cleared 70 mines over a period of 48 hours under heavy fire without rest in North AfricaMilitary Medal, G.VI.R. (1858429 L. Sjt. W. F. T. Beet. R.E.); 1939-45 Star; Africa Star; Italy Star; Defence and War Medals 1939-45; Army L.S. & G.C., G.VI.R. (1858429 Spr. W. F. T. Beet. R.E.), mounted court style for wear, light contact marks, very fine (7)M.M. London Gazette 23 September 1943, the original recommendation states:'This Sgt. was attached to my Bn. from 23rd. Fld. Coy., R.E. for the attack on Pt. 134 and GRICHEL OUED on 23rd April. During the period of consolidation when it was necessary to find and clear a German minefield on the track leading to GRICHEL OUED, this Sgt. behaved with great efficiency and devotion to duty and did all and more than was demanded of him and his sub-section with complete disregard for his personal safety.The above minefield was the first German field met with by any member of 23rd Field Company R.E.When he had completed his task of gapping and marking the field, L/Sgt. Beet had been leading his sub-sec. for 48 hours without sleep, and for a large proportion of this time he was under fire. He had actually lifted 70 mines of which 26 were "booby trapped" and 16 A. Pers. Mines.On 30th April L/Sgt. Beet was in charge of a minefield gapping party near the GABGAB gap. The party was under intermittent fire, and a mortar shell eventually wounded four of his party including himself. He refused to leave the site until the other three wounded had been attended to and he received a direct order from Officer i.c work to go.'William Frederick Taylor Beet enlisted on 5 May 1921 with the Royal Engineers as a Boy. He reached his majority on 10 June 1924, being advanced Sapper and posted to 'D' Company, T.B. Royal Engineers. Seeing service over the next decade he was posted to 23rd Field Company on 14 September 1939, this formation saw action during the Fall of France in 1940.Embarking with them for North Africa on 26 March 1943 Beet was to earn his award just the next month, under the most trying circumstances imaginable. He was later to serve with the unit in Italy from December 1943 however did not join them in Palestine in 1945.…
An extremely rare Edward VII gallantry K.P.M. awarded to Senior Constable J. C. Gates, New South Wales Police Force, the first Australian police officer to be so honoured and one of just four to receive the Edwardian issueIn his gallant pursuit of an armed burglar in North Sydney in April 1909, he exchanged fire until the latter ran out of ammunition, following which he closed with him to make an arrest: in the ensuing struggle, Gates was severely beaten about the head with the burglar's empty revolver, his wounds requiring 23 stitchesKing's Police Medal, E.VII.R., on gallantry riband (J. C. Gates, Sen. Const., N.S. Wales P.), minor edge bruises, good very fineK.P.M. London Gazette 14 January 1910.James Charles Gates was born in Christchurch, New Zealand on 28 February 1885, the son of a distiller. Opting for a new life in Australia when a teenager, he was working as a blacksmith when he enlisted in the New South Wales Police as a Constable.By the time of his K.P.M.-winning exploits in North Sydney, Gates had been advanced to Constable 1st Class but, as reported in various newspapers, he was about to receive accelerated promotion to Senior Constable.The incident in question commenced in Carabella Street, on the heights overlooking Neutral Bay, when an armed burglar broke into the house of Mr. Russell Sinclair in the early morning hours of 1 April 1909. Alerted by a lodger to the burglar's presence, Sinclair gave chase and a violent struggle ensued, in which he was twice shot in the groin. The burglar then made off down the street. Here, then, the moment at which Gates arrived on the scene. A newspaper report takes up the story:'It was after his escape into the streets that the fugitive waged another fight, this time with the constable who arrested him. When Constables McDonald and J. C. Gates, having been informed of that had occurred, proceeded to the locality, Gates saw a man near Milson's Point ferry. He watched the man, and at last he accosted him near Jeffrey Street. The man, who kept his right hand in his pocket, replied that he was on his way to visit someone in Carabella Street. The constable asked him why he kept his hand in his pocket, whereupon the man drew a revolver, fired, and then bolted. The shot missed Gates, who started off after the man, who, while he ran, turned and fired again twice, but still without effect. Constable Gates then fired, and an exchange of shots was kept up. The policeman was not hit but it was afterwards shown that one of his bullets grazed the fugitive's neck, causing a slight flesh wound. Gates, still in pursuit, reached his quarry near Livingstone Lane, and a hand-to-hand fight ensued.The man hit Gates a blow with the butt end of his revolver, and partially stunned him, but the Constable never allowed his prisoner to elude him, and was all the time endeavouring to hand cuff him. The Constable was furiously attacked, blow after blow being delivered about his head with the butt end of the revolver, and at length the man actually got free, but Gates, gallantly refusing to be beaten off, followed him and was joined by a civilian who had been alarmed by the noise of the conflict. Finding the chase hot, the fugitive dashed down some steps into an area in Fitzroy Street, and here he was finally captured, the Constable getting the hand cuffs on him.'The gallant Gates was duly awarded the K.P.M. as well as being advanced to Senior Constable. He was also presented with a Testimonial by the Mayor of North Sydney. His assailant - James Frederick Crook - was sentenced to death, a sentence later commuted to life.Gates died at Ghatswood in the northern district of Sydney in July 1955; sold with copied service record and newspaper reports.…
The campaign group of seven awarded to Major J. G. Forbes, King's Shropshire Light Infantry, who took the Hong Kong Plague Medal in gold when forming part of 'The Whitewash Brigade', being called out against the 'Black Death' during 1894; Forbes was no stranger to the risks posed by this deadly disease and acted as pall-bearer to brother officer Captain Vesey, who lost his life to the bubonic plagueQueen's South Africa 1899-1901, 4 clasps, Cape Colony, Paardeberg, Driefontein, Transvaal (Capt. J. G. Forbes. 2/Shrops. L.I.); King's South Africa 1901-02, 2 clasps, South Africa 1901, South Africa 1902 (Capt. J. G. Forbes. Shrop. L.I.); 1914-15 Star (Major J. G. Forbes. Shrops. L.I.); British War and Victory Medals (Major J. G. Forbes.); 1911 Coronation (Major J. G. Forbes), privately engraved naming; Hong Kong Plague 1894, gold issue, unmounted (Captain J. G. Forbes, S.L.I.), in red leather Wyon, Regent St, London case, the first six mounted as worn, good very fine (7)Provenance:Spink, September 1963 & August 1986.John George Forbes was born on 2 February at Melbourne, Victoria, the son of John G. Forbes, a barrister. By 1881 the family were living in Cheltenham, with young Forbes a scholar, likely at Cheltenham College. He then went to the Royal Military Academy Sandhurst and was commissioned into the Shropshire Light Infantry in June 1886. Joining the station at Hong Kong, being a keen horseman, he was a member of the Hong Kong Polo Club by 1893 and Adjutant of his unit.Whitewash BrigadeA virulent epidemic of bubonic plague broke out in Hong Kong in early May 1894. Recognising the danger, the Governor, Sir William Robinson, K.C.M.G., gathered all the resources available to him, both military and civil, to combat the threat. Special bye-laws were quickly passed and implemented, and temporary plague hospitals were opened. The task of finding, isolating, disinfecting and cleansing infected households was directed by Mr F. H. May, the Captain Superintendent of Police and supervised by Mr J. H. Crook the Sanitary Surveyor. To supplement the local authorities and native labour, Officers and men of the Shropshire Light Infantry and Royal Engineers were drawn in to help with the cleansing operations, and Volunteers for house-to-house visitations were sought amongst the civil population. The population in infected areas were removed and infected houses were rigorously cleansed - floors disinfected, walls, woodwork and furniture thoroughly lime-washed, and bedding, old clothing, old woodwork and general rubbish burnt. Elsewhere, doctors, nurses and ancillary staff worked heroically amongst the sick and dying.Forbes volunteered and went out on plague duties to relieve other officers as a house-to-house visitor, and doubtless would have followed the official guidelines in helping to combat the spread of the Plague:'1. Keep separate clothes for working in, which should be changed on returning off duty and kept hung up in the air and sun when not in use.2. On returning off duty wash the hands in water and Jeyes’ fluid (1 in 20), and if possible take a bath of the same solution.3. Also rinse the mouth out with Condy’s fluid and water (one teaspoonful to one quart of water).4. Saturate the handkerchief with Eucalyptus oil when going on duty and apply it frequently to the nose if in an infected house.5. Smoke.’Despite all the precautions taken, over 2,500 people, mainly Chinese, contracted the plague, with 2,317 deaths attributed to the disease, a fatality rate of over 90%. That saw a brother officer of the unit, Captain Vesey pass of the plague. Forbes was a pall bearer at his funeral on 5 June when he was buried in the Happy Valley Cemetery.The plague subsided with the arrival of cold weather, and restrictions were lifted in early September. On 28 September 1894 a public meeting was held at City Hall for the purpose of considering what steps should be taken to recognise the services rendered by the community in combating the plague, and ultimately it was decided that a medal should be awarded, in both gold and silver. His name was one of approximately 13 officers who would take the medal in gold.He served with the 2nd Battalion during the Boer War in South Africa (Queen's Medal & 4 clasps, King's Medal & 2 clasps) and by 1907 was in command of the Depot Troops at Shrewsbury.With the outbreak of the Great War, Forbes would see himself proceed overseas as Second-in-Command of the 5th Battalion. They had been formed at Shrewsbury in August 1914 as part of K1 and came under orders of 42nd Brigade in 14th (Light) Division. Moved initially to Aldershot, and then went on to Chiddingfold in March 1915, they landed on 20 May 1915 at Boulogne. Forbes would remain in the front lines with his men until removed to England, having celebrated his fiftieth birthday at the start of that year. In the following years his name appears as having been involved in the prosecution of Military Court Martial proceedings at home. He was further involved in the compilation, publication and distribution of the Regimental History of the Great War. The good Major, who later lived at 51a Jermyn Street, died on 12 October 1937 as is commemorated upon a marble memorial at St Chad's, Shrewsbury.The Plague Medal - how many?No complete medal roll for the Hong Kong Plague Medal is known to exist, with much of the Colony’s archival material having been destroyed during the Second World War; consequently, the number of medals awarded is a matter of conjecture. Mr. F. Pridmore, in an article for the Spink Numismatic Circular, August 1954, states that 137 gold medals were awarded to civilians, together with 13 being awarded to the officers of the King’s Shropshire Light Infantry; Jerome Platt, Maurice Jones, and Arleen Platt in The Whitewash Brigade again estimate that 137 gold medals were awarded to civilians, and increase the number awarded to the military garrison to 46, as well as giving a total of 636 silver medals awarded. It is the opinion of the cataloguer that the figure slightly shy of fifty was the total amount of awards struck and issued in gold, not in excess of one hundred.It is however the result of an incorrect transposition in a previous newspaper article that these figures have been calculated. On reflection, it would also surely have been impractical - and unlikely given the amount of individuals who would possibly qualify - for such a large distribution in gold. Many have likely to have been scrapped for the value of the gold content by now, but around 20 known extant awards in gold have been recorded over the years.Given that the medal, as the gift of a Colonial Government and not one proceeding (or depicting) the monarch, was not authorised for wear. It could be accepted and retained, but as a commemorative/gift, could not be worn in uniform and thus most gold medals remained unmounted, much like this very example; sold together with two cap badges and images of the recipient.…
'Now, gentlemen, let us do something today which the world may talk of hereafter!Thus spoke Rear-Admiral Cuthbert Collingwood from the deck of his flagship, H.M.S. Royal Sovereign, prior to the Battle of TrafalgarThe Naval General Service Medal awarded to Able Seaman E. Kendall, Royal NavyNaval General Service 1793-1840, 1 clasp, Trafalgar (Edward Kendall.), good very fineProvenance:Seaby, June 1953.Spink, December 1972.Edward Kendall was born in London around 1778 and was 27 years old when he served as an Able Seaman aboard the H.M.S. Royal Sovereign during the Battle of Trafalgar.Royal Sovereign was a 100-gun first rate ship of line and was launched at Plymouth in 1786, over a decade after she was laid down in 1774, and was the only ship built to her specific design. Reportedly slow and difficult to manoeuvre, she was nicknamed the 'West Country Wagon' by her crew.Prior to serving at the famed Battle of Trafalgar, Royal Sovereign enjoyed an active role during the French Revolutionary Wars. She served as part of Admiral Richard Howe's fleet during the Glorious First of June, the first fleet action of the War, where she was the flagship of Admiral Thomas Graves' vanguard squadron. This resounding tactical victory saw Admiral Howe issue the unorthodox order for his ships to turn and breach the French line, rake the enemy ships and engage them directly. Royal Sovereign pulled too far into the line and suffered a heavy pounding from enemy ship Terrible, with Admiral Graves mortally wounded and dying during the course of the battle. Terrible fell out of the line and Royal Sovereign next engaged Montagne. Seven enemy ships were sunk or captured but the British lost none.Now the flagship of Vice-Admiral William Cornwallis, Royal Sovereign was further engaged in the conflict known as 'Cornwallis' Retreat'. In June 1795, a French fleet of twelve ships of the line and eleven frigates gave chase to Cornwallis' squadron of five ships of the line and two frigates. After a day's chase the rearguard came within range of the enemy, and rather than abandon part of his squadron Cornwallis stood his ground to counterattack with all his might. The Vice-Admiral steered Royal Sovereign in between the French and British forces, meeting the enemy with a raking fire. The Battle ended when French Admiral Villaret de Joyeuse mistakenly believed the British Channel Fleet was approaching and subsequently ordered his fleet to withdraw, thus allowing Cornwallis to escape.Royal Sovereign was further involved in a notable altercation on 17 March 1796 when the transport ship Bellisarius collided with her while en route to the West Indies and sank almost instantly. The Battle of TrafalgarH.M.S. Royal Sovereign held the distinction of being flagship of Vice-Admiral Collingwood, Rear-Admiral Horatio Nelson's second-in-command at that famous sea battle off the coast of Trafalgar, Spain on 21 October 1805. She led one column of warships during the conflict while Nelson led the other, and was the first ship of the fleet to enter the action.Recently re-coppered, Royal Sovereign was faster than the other ships present and was the first to break the enemy line in accordance with Nelson's unorthodox plan to approach the allied line with his fleet arranged in two columns, which would cut the allied line and force one-on-one fighting.As Royal Sovereign gallantly sailed alone towards the enemy and made to engage the massive Spanish three decker Santa Ana, Collingwood remarked to his Captain, Edward Rotheram, "What would Nelson give to be here?". At roughly the same time, his friend Nelson reportedly pointed to her and exclaimed, "See how that noble fellow Collingwood carries his ship into action!".Collingwood's well-trained crew aboard Royal Sovereign fired such a rapid volley at Santa Ana that four allied ships quickly came to her aid, with Royal Sovereign first receiving fire from Fougueux before being joined by Indomptable, San Justo, and San Leandro. Despite this assistance, Santa Ana suffered nearly 240 casualties and struck her colours to Royal Sovereign at 2:20 that afternoon.Hemmed in at all sides by the enemy, Royal Sovereign suffered significant damage before she could be relieved by the remainder of the British fleet. She had lost her mizzen and main masts, most of her rigging, and suffered damage to her foremast and was no longer manoeuvrable. Even so, she continued to fire at the enemy from her port-side guns. Collingwood himself also suffered a wound to his leg whilst on deck, but was lucky in that he was only one of three officers on her quarterdeck who lived to see the end of the Battle.Following the death of Nelson at around 4:30pm, Collingwood assumed command of the fleet as commander-in-chief. Collingwood removed to H.M.S. Euryalus as a consequence of Royal Sovereign being, in his words, "perfectly unmanageable" after sustaining too much damage to continue as flagship. While Nelson's final command prior to his death had been for the fleet to anchor in advance of an oncoming gale, Collingwood disagreed and focused on those vessels still able to anchor and survive the storm. He had Royal Sovereign towed away while she was still able to stay afloat. She sustained 141 casualties over the course of the Battle.After TrafalgarFollowing the battle, missing her mizzen and mainmasts and most of her rigging, Royal Sovereign returned to Plymouth to be repaired and refitted. She thereafter returned to duty as part of the Mediterranean Fleet and participated in the ongoing blockade of Toulon. In November 1811 she was ordered to join the Channel Fleet, later being converted to harbour service as a receiving ship. Renamed Captain in 1825, she was eventually broken up at Plymouth in 1841. Four of her cannons were incorporated into the Collingwood Memorial in Tynemouth, where they may be seen to this day.Little is known about the fate of Kendall aside from his service at Trafalgar, only that he is confirmed on the roll as serving with Royal Sovereign during the battle and that he lived to claim his medal; sold together with copied medal roll.…
The superb Great War 'successful escapers' M.M. group of four awarded to Private H. Wilson, 1st Battalion, Coldstream Guards, who was taken Prisoner of War at the First Battle of Ypres in 1914 and whose remarkable escape is summarised in the archive of the Coldstream GuardsMilitary Medal, G.V.R. (8617 Pte. A.Cpl - H. Wilson. 1/C.Gds.); 1914 Star (8617 Pte H. Wilson. C.Gds:); British War and Victory Medals (8617 A - Cpl. H. Wilson. C.Gds.), mounted as worn, light pitting, very fine (4)Henry Wilson was born in 1890, a native of Hull and enlisted on 25 February 1910, his initial service proved uneventful however he did earn an Army swimming certificate in 1911. Joining the Army Reserve he returned to Hull and joined the Police Force there. Wilson was still there when he was mobilised on 6 August 1914 for service in the Great War.Entering the war in France on 13 August 1914, he was appointed Lance Corporal after the Retreat to the Marne and took part in the Battle of the Aisne. They were stationed near Langmark when the First Battle of Ypres began and saw heavy fighting before being moved to the Menin Road on 26 October. Three days later a major German attack began in that direction, they drove back the other units in the area and, by the time reinforcements came up, the 1st Battalion had effectively ceased to exist.Wilson was wounded in the left side and taken prisoner of war, being taken to the camp of Schneidemuhl. Unfortunately, the conditions at the camp were not much better than in the trenches with typhoid rampant and the chief medical officer attempting to curb it by starving the prisoners. The only food they received came from the Red Cross via the Swiss city of Bern.Fortunately, Wilson was able to survive the camp long enough to be sent to Krehendberg camp where he was ordered to join the work parties on the local farms. He escaped one of these parties on 27 July 1917 and made his way through the mountainous area to the south of the Black Forest. After a two-day trek Wilson reached the Rhine, across the river lay neutral Switzerland and the prospect of freedom, however the river bank was patrolled and the river itself was a difficult prospect.Waiting until nightfall he removed his jacket and boots and began the swim, a strong current swept him along downriver. Wilson managed to struggle out of his trousers and thus unencumbered began to make progress, when he eventually made the Swiss bank he was two miles downriver from his start point. Encountering a Swiss civilian he was taken to a Police Station where he explained who he was and made contact with the British Legation.While there awaiting repatriation Wilson wrote a letter to the Honorary Secretary of the Coldstream Guards Prisoners Fund stating:'Dear Hon SecJust a few lines thanking you for the parcels I received from you while I was in Germany & to let you know that I shall not require any more as I have escaped from Germany. I ran away from work at 4:00pm July 27th swam across the Rhine & landed in Switzerland about 12.30 am July 30th. I am now in Bern & have to remain here for a few days at least. I hope to return to England shortly.'He was repatriated and saw Home Service for the rest of the war; sold together with copied research.The papers of Corporal Henry Wilson are available as part of the Liddle collection at the Brotherton Library, University of Leeds. A typed summary of their contents was prepared by the archive of the Coldstream Guards.…
The 'Great War' M.C. group of eight awarded to Honorary Colonel J. G. Chapple, Royal Army Ordnance Corps, later Royal Electrical and Mechanical Engineers, who served on the Western Front inspecting and repairing artillery, later becoming the Officer in Command of all Ordnance Workshops in Mesopotamia during the Iraqi Revolt, later he served in France during the 1940 campaignMilitary Cross, G.V.R.; 1914-15 Star (Lieut. I. O. M. J. G. Chapple. A.O.D.); British War and Victory Medals (Major J. G. Chapple.); General Service 1918-62, 1 clasp, Iraq (Major J. G. Chapple. R.A.O.C.); 1939-45 Star; Defence and War Medals 1939-45, mounted as worn, overall good very fine (8)Provenance:Purchased Spink Numismatic Circular, March 1979.M.C. London Gazette 4 June 1917.John Gardiner Chapple was born in Mauritius on 11 February 1886, the son of James Chapple. He was initially schooled privately before joining the Woolwich Polytechnic in 1902 and remaining there until 1910. Chapple was initially employed as an Inspector of Royal Engineers Stores, Woolwich from 1910-1914 when he undertook a course at the Royal Military Academy Woolwich and was commissioned Lieutenant (Inspector of Ordnance Machinery Class III).Entering the war in France on 30 May 1915 his application for the Institution of Mechanical Engineers lists his duties at the time which included 'Inspection & Repair of Artillery & War Material'. Advanced Captain and Inspector of Ordnance Machinery Class II he was further appointed Works Manager of the Calais Workshops.Transferred to Italy in 1917 Chapple was further advanced Major and Inspector of Ordnance Class I on 7 March 1917. It was not long after this that he was awarded the M.C., likely for his services in France prior to transferring to Italy.Chapple was confirmed in the rank of Major on 5 November 1918 and remained in the Military after the war, being appointed Officer in Command of all Ordnance Workshops in Mesopotamia from 1920. This placed him in the region as both Senior Inspector of Ordnance Machinery and Technical Advisor during the Iraqi Revolt, remaining there until 1922.Returning to Britain he was appointed back to the Royal Engineers Stores at Woolwich as a Chief Draughtsman where he was responsible for designing new stores for the War Office. Joining the Air Ministry in 1926 Chapple was working at R.A.F. Halton as the stationed Electrical and Mechanical Officer in 1926.Still serving as a Major in 1939 whilst living in Nottinghamshire he saw service in France in 1940 however did not return to the continent in 1944. Chapple was discharged having reached the age of liability on 27 September 1946 with the honorary rank of Colonel. He retired to Portsmouth where he died in April 1972; sold together with copied research.…
The campaign group of four awarded to Captain D. J. R. Simson, Royal Navy, who was killed by a German sniper on 23 May 1940 while serving aboard H.M.S. Keith at Boulogne when the port was infiltrated by German troops; he also received a posthumous 'mention'Naval General Service 1915-62, 1 clasp, Palestine 1936-1939 (Capt. D. J. R. Simson. R.N.); 1939-1945 Star; Atlantic Star; War Medal 1939-45, with M.I.D. oak leaf, these in box of issue and with named Condolence slip, extremely fine (4)M.I.D. London Gazette 27 August 1940.David James Robert Simson was born on 7 September 1892, later studying at Osborne and then Dartmouth, taking the King's Medal. He was promoted Midshipman on 15 January 1910 and served aboard Russell and Lancaster in the Mediterranean and with Lion during her first commission. Later being further advanced Sub-Lieutenant on 15 April 1913, during the Great War he served on the destroyer Acasta and battleship King George V at the Battle of Jutland.From March 1918 he first held command on Usk. Simson was promoted to Lieutenant-Commander on 15 January 1923, Commander on 30 June 1928, and between 1929-30 was the Executive Officer at the boys' training establishment at Shotley. After this time he returned to serving aboard destroyers and commanded, among other vessels, Vanquisher in the Mediterranean, Valorous in the Home Fleet, and between 1934-35 the cruiser Cumberland in China. During the Naval Review in 1935 Simson commanded Thanet before commanding Vivien and Winchelsea and from May 1936 the new destroyer Grenville. He was promoted Captain on 30 June 1936 and was later placed in command of Codrington from 24 August 1939 until 26 November and was then in charge of Keith from 15 February 1940.On 10 May 1940, the Germans launched their invasion of France and the Low Countries. That day Keith and her sister Boreas escorted the light cruisers Arethusa and Galatea as they carried bullion from the Dutch port of Ijmuiden to the United Kingdom for safe keeping. On 12 May, she returned to the Hook of Holland in the Netherlands to evacuate Allied troops. After the destroyer Whitley had to be run aground on 19 May when she was damaged by German aircraft, she was scuttled by Keith. Keith was one of three destroyers on 21 May that evacuated 468 civilians from France. Two days later she was in Boulogne-sur-Mer, loading British troops at the Gare Maritime to be evacuated and was attacked by German troops who had infiltrated the port area. Simson was shot by a sniper and several crew members and a dozen soldiers were also killed.He is commemorated on the Chatham Naval Memorial. Keith sailed for the UK immediately afterwards and was later active during Operation Dynamo. She was sunk off Dunkirk by German air attacks on the morning of 31 May 1940.Brigadier W. A. Fox-Pitt, who served as commander of the 20th Guards Brigade to defend Boulogne and was subsequently awarded a D.S.O., wrote to Simson's brother, Lieutenant-Colonel A. M. Simson on 20 August 1946:'My only means of communication with England during the battle was through H.M. Ships so that if there was no destroyer in, I was completely out of touch. The last destroyers left Boulogne during the night of the 23/24th and I was out of touch with England until H.M.S. Keith came in about 3p.m. By this time I had ordered a withdrawal into a closer perimeter round the Harbour in order to prevent the Germans getting round my northerly flank and cutting us off.I went aboard the Keith and had a conference with Simson and discussed the situation and sent off certain signals explaining the progress of the battle. I also had a very welcome cup of tea and gave one of the officers a letter to post for me in England. We were both pretty certain then that it was a waste of life to continue to hold Boulogne as my casualties were mounting pretty rapidly.However, a signal arrived while I was on board from the Prime Minister saying "You will evacuate all non military personnel (Pioneer Corps etc), the 20th Guards Brigade will fight it out". I then left the Keith and went and saw my Battalion Commanders and gave further orders for holding the town. I was away about two hours and then returned to the Keith, for further orders. While on board I received the signal telling to evacuate. As it was getting late I went ashore immediately to get my orders out and understood that the destroyers would put out and come back again after dark for the evacuation. I had only just left the ship when the air attack started and during the attack Simson was killed. The destroyers left the port as soon as they could and I continued with my arrangements for evacuation. I did not know that Simson had been killed until the destroyers came in later. Condor of the Whitshed, was then left in command of the Flotilla. Just before dark the destroyers came in again and I was told that I must evacuate immediately. This meant putting my plan in motion very quickly, but eventually all the troops were evacuated by about 2 a.m. on the 25th.My recollections of your brother are pretty vivid. I found him most helpful in concocting signals to England. He was at all times thoroughly calm and collected and very quick to grasp the situation on shore. He realised the importance of the destroyers as my only link with Dover, and I fear it may have been for this reason that he stayed in the port so long, as the destroyers were a very tempting target. I don't remember the Germans being within small arms range of the Keith at the time of the air attack, but the aircraft were machine gunning as well as dropping bombs. The real battle between the destroyers and the land targets took place later when the destroyers completely silenced the Germans for the rest of the night and I saw a German tank knocked out by one of their guns myself.'Sold together with the following archive comprising:i)The handwritten letter to Mrs Simson from Admiral Sir B. H. Ramsay, dated 25 May, written from Dover expressing his deepest sympathy upon his death.ii)Officer's bicorn hat, epaulettes and sword belt in named tin, together with Greatcoat Epaulettes.iii)Two sets of his pre-Second World War miniature medals, with riband bars.iv)Silver Oar rowing prize for the VIIIth Flotilla Officers Race 1925 H.M.S. Venturous, silver napkin ring and silver clothes brush.v)Letter to his wife and that to his brother from Fox-Pitt, besides photographs and assorted calling cards (5), newspaper cutting, Blue Lists (2), The List 1940, black armbands (2), besides a four leaf clover and lucky heather.…
The Bronze Star group of ten to Indirect Fire Infantryman (Mortarman) W. J. Scovil, 2nd Battalion 8th Cavalry who served as part of 1st Cavalry Division (Airmobile)United States of America, Bronze Star with V emblem (William J. Scovil) engraved; Purple Heart; Air Medal, bronze (William J. Scovil) engraved; Commendation Medal with V and oak leaf emblems (William J. Scovil) engraved; Good Conduct Medal (William J. Scovil) engraved; National Defence Service Medal; Vietnam Campaign Medal with 1960- clasp; Vietnam, Campaign Star; Vietnam, Cross of Gallantry with Palm; Vietnam, Civil Action Honour Medal, mounted on a framed display, very fine (10)William James Scovil studied at Ullman High School, Birmingham, Alabama, he received a Diploma and completed his studies in 1968.Joining the United States Army at Montgomery, Alabama, on 8 April 1969 he served at 2nd Battalion 5th Advanced Infantry Training (A.I.T.) Brigade at Fort Polk, Louisiana from 15 June 1969.Posted to United States Army Pacific (USARPAC) on 16 August 1969 he saw service in Vietnam from 6 September 1969 as part of the 1st Cavalry Division (Airmobile) in the role of an Indirect Fire Infantryman (Mortarman) with the 2nd Battalion 8th Cavalry Regiment (Airmobile).1st Air Cavalry Division 1969 -1970In late 1968, the Division moved and set up operations in III Corps at the other end of South Vietnam in late 1968. They were still there when Operation Cheyenne Sabre began in areas northeast of Bien Hoa in February 1969. Their actions here were to prove decisive and by the end of the year the enemy's domination of the northern areas of III Corps had been smashed - thoroughly.When Operation Rock Crusher was launched on 1 May 1970, the First Team was "First into Cambodia" hitting what was previously a Communist sanctuary. President Nixon having given the go-ahead for the surprise mission. They pushed into the 'Fish Hook' region of the border and occupied the towns of Mimot and Snoul whilst troopers scattered the enemy forces, depriving them of much needed supplies and ammunition.The men of the 2nd Brigade found an enemy munitions base that they dubbed 'Rock Island East' on 8 May. The Mission to Cambodia, ending on 30 June, far exceeded all expectations and proved to be one of the most successful operations of the First Team. All aspects of ground and air combat had been utilised and the enemy had lost enough men to yield three NVA divisions and enough weapons to equip two divisions. Further successes included a year's supply of rice and corn seized, uncommonly large quantities of ammunition taken, including 1.5 million rounds for small arms, 200,000 anti-aircraft rounds and 143,000 rockets, mortar rounds and recoilless rifle rounds. As well as 300 trucks, a Porsche sports car and a plush Mercedes Benz sedan.The campaign was to have severe political repercussions in the United States for the Nixon Administration however and pressure was mounting to remove America's fighting men from the Vietnam War. Although there would be further assault operations, the war was beginning to wind down for many troopers.Posted away from Vietnam on 5 September 1970 Scovil began his return to the U.S.A. on 22 September 1970 and on 11 October he was an Indirect Fire Crewman with the 6th Battalion of 32nd Armour based at Fort Knox, Kentucky, where he completed his Army service on 8 April 1971.Sold together an original archive comprising:(i)Combat Infantryman Badge(ii)Air Assault Badge(iii)Valorous Unit Award 1st May - 29th May 1970 for "Fish Hook" region Cambodia(iv)Dress Cap Badge(v)Specialist 4th Class patch (2)(vi)Riband bar for uniform(vii)1st Air Cavalry Division patch(viii)8th Cavalry patch(ix)8th Cavalry cap badge(x)Assorted copied research which shows various service details including medal entitlement.(xi)Safe Conduct Pass(xii)A further set of uniform medal ribands…
'A charming & handsome old man with one arm.So wrote the niece of the gallant Colonel KnoxAn outstanding campaign pair awarded to Colonel K. Barrett, 13th Regiment of Foot (1st Somersetshire) (Prince Albert's Regiment of Light Infantry), a long-served and most gallant officer who served on campaign in the Caribbean, Upper Canada and Burma - having his arm blown off in the attack on the Great Pagoda in July 1825 in the lastMilitary General Service 1793-1814, 2 clasps, Martinique, Guadaloupe (Knox Barrett, Ensn. 13th Foot.); Army of India 1799-1826, 1 clasp, Ava (Bt. Captn. K. Barrett, 13th Foot.), short-hyphen reverse, officially impressed naming, heavy edge bruising, very fine (2)Knox Barrett was born circa 1783, the son of William Barrett, High Sheriff of Sligo, of Culleenamore House. The Sligo Independant of July 1882 gives more detail:' He joined in 1805 from the North Mayo Militia, obtaining an ensigncy in the gallant 13th Regiment of Foot. This regiment, when in India saw much service, and Colonel Barrett, then a Lieutenant, showed much pluck and coolness on the battle field. At Rangoon, when the English army under General Dale fought well and bravely, Colonel Barrett led his Company in the thickest of the fight, and had his right arm shot off. He was specially mentioned by his Colonel, afterwards the great and good General Havelock as being a brave officer. Of course, the loss of his arm obliged him to retire from the Army, and General Havelock, whose friend and companion he was, parted from him with regret. He possessed medals and claps for Ava, Guadeloupe, Martinique, India etc. Since he left the army, he came to reside in Sligo.'Barrett has a remarkable record of service in the Caribbean, North America and in India. Having shared in the actions at Martinique in October 1809, he was present at the capture of Guadaloupe and was then subsequently posted to Upper Canada with his unit. Their Light Company was stationed at le Aux Noix and a detachment went to the blockhouse of Lacolle Mills - when they shared in the famous defence of that place in March 1814.Furthermore, Barrett would have been with his unit when they crossed Lake Champlain to attack Plattsburgh in New York, sharing in the final acts of the War of 1812. They departed the scene in July 1815. He would then share in the events in India, being unfortunate to have his '...arm blown off' during the attack on the Great Pagoda in the First Anglo-Burmese War. On 5 July 1825 the unit also suffered one man killed and seventeen other ranks wounded in action besides Barrett.Retired on account of his wounds, he was provided with a pension of £70 for his wounds. Returned to his native Sligo, he took up various posts, including as Justice of the Peace, Superintendent of the gaol, a member of the Sligo Harbor Commission and sat on the Dispensary Commission. Having married Anne Rice in 1827, the pair had no children but were always known for their generosity to their numerous nephews and nieces. The good Colonel died on 10 July 1882 and is buried in the family tomb at St John's Churchyard. His obituary notice gives the final word:'Our obituary notices of to-day announce the death of this gentleman who lived to a patriarchal age, being nearly a century old when he breathed his last at his residence, Rathanna, near this town. It may be well said that by his death a link connecting the present generation with the past – the long past – a severed, for when many grandfathers of today were leading strings Colonel Barrett was fighting for his King and country on the burning plains of India...In private life he was distinguished for his mildness of disposition and goodness of heart.'…
The Second World War campaign group of four awarded to Guardsman K. O. Gammell, Grenadier Guards; reputedly the tallest man in the Brigade of Guards (standing at 6ft. 7 1/2in. tall) he was destined for a fine academic career but instead enlisted in the British Army upon the outbreak of war, tragically he died on Christmas Eve 1943 of wounds received during the Italian Campaign1939-45 Star; Africa Star, clasp, 1st Army (2622616 Gdsmn K.O. Gammell Grenadier Guards); Italy Star; War Medal 1939-45, all privately and contemporarily engraved '2622616 Gdsmn K.O. Gammell Grenadier Guards' in upright capitals, mounted court-style for wear, sometime lacquered, about extremely fine (4)Kenrick Orm Gammell, son of Kensington and Doris Gammell, was born in Bedford on 18 May 1910. Clearly academically gifted, after education at Bedford School (a boys public school founded in 1552) he went up to Gonville and Caius College, Cambridge (1928-31) and graduated with a B.A. Becoming a schoolmaster in Essex, the outbreak of war in September 1939 thwarted his plans to take up a post as Headmaster of Akley Preparatory School and instead he enlisted in the Grenadier Guards, being posted to the 6th Battalion after his basic training.Formed in 1941, the 6th Battalion was posted to Syria in September 1942 and saw action in the Tunisia campaign before participating in the invasion of Italy a year later. On 23 October 1943, Gammell was severely wounded in an action near Naples and evacuated to North Africa. Sadly he succumbed to his injuries on 24 December and is buried at Bone Military Cemetery, Annaba, Algeria. In addition to an obituary in the 'Bedfordshire Times and Standard' (7 January 1944), his grave bears the moving epitaph: 'Thoughts Too Deep For Words. A Very Dear Only Son. He Was 6 Feet 7 1/2 Inches Tall'.Sold together with a Guards Depot Recruits Musketry prize medal in the form of a watch-fob, engraved Rct. K. Gammell. For his father's Special Constabulary Long Service Medal, see Lot 107.…
The rare and remarkable 'Tiddim Defence of Point 6052' M.C. and 'Battle of Imphal' Second Award Bar group of five awarded to Captain C. F. V. Martin, Oxfordshire and Buckinghamshire Light InfantryMilitary Cross, G.VI.R., the reverse dated '1944', with Second Award Bar dated 1944; 1939-1945 Star; Burma Star; Defence Medal; War Medal 1939-45, mounted for wear, sold together with the named Buckingham Palace forwarding slip for the Military Cross and Second Award Bar and a further archive, good very fine (5)M.C. London Gazette 18 May 1944, the original recommendation states:'While in command of a company on pt. 6052 on the 26th of January 1944, the enemy put in a persistent attack from 1745 hours to 1830 hours, which was repulsed with heavy losses. At 2300 hours the enemy again attacked with even more determination but was again driven back. During both these attacks, Captain Martin ran from post to post in the open, directing the fire and encouraging the men, regardless of his personal safety. Throughout the 27th and the 28th, the enemy sent frequent harassing parties to wear down our defences and to prevent our men from sleeping. On the 29th of January, our position was again very heavily attacked, this time by two enemy companies, from 0530 hours to 1030 hours. Although the position was thinly held, our casualties equivalent to one platoon, and the men tired through three sleepless nights, the enemy was driven back time and again with very heavy losses estimated at 200 killed and wounded. Although completely without sleep during these four days, Captain Martin went from trench to trench, encouraging the men and urging them to hold on, despite close range grenade, small arms and very heavy mortar fire. When the enemy broke through the wire and threatened to swamp the defences, he personally organised and led a counterattack which, by determined hand to hand fighting wiped out all the enemy who had broken in. Captain Martin's splendid example of personal gallantry and leadership in the face of heavy odds, his spirit of endurance and determination to hold out, inspired all ranks to resist at all costs, over a period of four days, a persistent enemy attempt to capture a position of extreme tactical significance'Second Award Bar London Gazette 5 October 1944, the original recommendation states:'On the morning of the 26th of May 1944, Captain Martin was leading a Company taking part in the attack on Red Hill RK 224488.In the initial stages of this attack Captain Martin was wounded leading his Company under heavy MMG fire on to the objective, but ignoring his wounds this officer personally led a grenade throwing party to wipe out a Japanese Bunker, which was holding up the advance of his company. With complete disregard for his own safety and despite his wounds this officer approached the bunker, the occupants of which had been catching our grenades and throwing them back, and by waiting 3 seconds after the cap of the grenade had been struck before he threw it, succeeded in wiping out the bunker and thereby clearing the way for the advance. In doing this Captain Martin was again wounded, but continued to lead his Company forward until he collapsed from loss of blood.This magnificent example of gallantry and selfless devotion to duty under heavy fire was not only a supreme inspiration to every man in the Company, but a vital contributory factor in the success of the attack.'Clifford Frederick Victor Martin was born in Oxfordshire on 17 July 1919, the son of Captain Victor and Rose Martin. Granted a Regular Army Emergency Commission and gazetted as a 2nd Lieutenant with the number 113619, he joined the Oxfordshire and Buckinghamshire Light Infantry on 16 January 1940.Martin then saw service out in India and Burma when on attachment to the Indian Army and serving with the 7th Battalion, 10th Baluch Regiment. He likely received his attachment to the 7th Battalion in the aftermath of the retreat from Burma in 1942, during which the Battalion had formed part of the 46th Indian Brigade in the 17th Indian Division. After withdrawing from Burma, the 17th Division then found itself stationed in Assam.They were not part of the failed First Arakan Offensive of late 1942 into the spring of 1943, but instead undertook intensive training to learn from the mistakes of the previous year in readiness to take the offensive against the Japanese in 1944 and 1945.The Defence of Point 6052Their first major operation occurred in January 1944, and it was Martin - then commanding a composite formation of 'A' and 'C' companies - who bore the brunt of it. It was for this period while serving as a temporary Captain that he was awarded the Military Cross for his gallantry during the defence of Point 6052.Martin's composite company was established on Point 6052, seven miles south of Tiddim, to form a patrol base. They launched several patrols to engage and identify the Japanese in the area and the perimeter of the base was at one point attacked but the company was able to hold on. This attack occurred on 26 January 1944, the day Martin earned his first Military Cross.It was estimated that the 7/10th Baluch killed more than 200 Japanese in the area, while themselves suffering only 3 killed and 10 wounded over the course of the month. The positions were dug in all round defences on ground of the 7/10th Baluch's choosing. This enabled them to repel the Japanese attacks, unlike at Pa-an in 1942, and showed that the retraining of the past 18 months had paid dividends.In the aftermath of his honour, Martin received a personal letter from General Slim, commander of the 14th Army, stating: 'I am very pleased to hear that your gallant action has been rewarded, and sent you my warmest congratulations on a well deserved honour.'The Battalion continued to send out patrols in the areas in front of and around Point 6052 in February and March, with the men and officers gaining valuable experience in operating as light infantry during this period. The Battalion, along with the 4/12th Frontier Force Rifles, withdrew along the Tiddim Road on 4 April in the face of increasing pressure during the Japanese advances and the repositioning in readiness for the Battle of Imphal.ImphalHaving retreated onto the Imphal Plain, they were sent to protect the Panel airstrip. The Battalion took over positions in the 'Catfish Box' area on 5 April, also at this point receiving reinforcements to create a fourth company and bring it up to strength as an ordinary infantry unit.A Company, under the command of now acting-Major Martin, was sent to Point 5846 on the Bishenpur-Silchar Road while the rest of the Battalion took the opportunity to re-organise and to incorporate the new company. The 7/10th Baluch moved to the 17th Divisional Box at Chingphu, north of Bishenpur, in mid-May as a response to increased Japanese pressure on the entrance to the Imphal Plain from the Bishenpur region.Red Hill PimpleThey began to dig in immediately upon arrival in their capacity as a protection of the divisional HQ. A series of patrols were sent out around the area as reports arrived of Japanese forces coming from the west, and a major clash ensued on 20 May involving one platoon on a ridge overlooking the divisional area. This force managed to hold out for more than 8 hours and successfully held up a major Japanese group. On 25th May, the Battalion was ordered to carry out an attack on Point 2926, 'Red Hill Pimple'. That evening, 3 Companies - A, B and C, respectively - moved to their jumping off positions, which included the ridge itself, without being heard or noticed by the Japanese.The A and C Companies were to attack the Japan…
The 'Trench Raid 1918' D.C.M., 'Asiago Plateau August 1918' Al Valore group of five awarded to Company Sergeant-Major H. Loughman, 2nd Battalion, Border Regiment, who rushed and cleared two machine gun posts during a raid in 1918Distinguished Conduct Medal, G.V.R. (6445 C.S.Mjr: H. Loughman. 2/Bord:R.); 1914-15 Star (6445 Sjt. H. Loughman. Bord. R.); British War and Victory Medals (6445 W.O.Cl.2. H. Loughman. Bord. R.); Italy, Kingdom, Al Valore Militare, silver issue (Altipiano D'Asiago H. Loughman 8-9 Agosto 1918), good very fine (5)D.C.M. London Gazette 15 November 1918, the original citation states:'For conspicuous gallantry and devotion to duty in a raid. He was with the leading platoon, and when the first lines of his company were held up by hidden wire and very heavy machine-gun fire, he dashed forwardwith a few men and rushed two machine guns one after another, killing or capturing the teams. This action enabled his company to reform and successfully rush the objective. He showed magnificent courage and rendered most valuable service.'Al Valore Militare London Gazette 29 November 1918.Herbert Loughman entered the war in France on 22 March 1915 with the 2nd Battalion, Border Regiment. The unit saw action at the battles of Neuve Chappelle, Aubers Ridge and Festubert, Loughman was noted as wounded in action in the Lancashire Evening Post casualty list of 15 October 1915. They saw heavy action on the Somme and at Passchendaele before being posted to Italy in 1918.There they were present for the Second Battle of the Piave River and later the fighting on the Asiago Plateau. It was there that Loughman won his Al Valore and likely also the D.C.M. The Whitehaven Advertiser and Cleator Moor and Egremont Observer in October 1918 states that he was awarded the D.C.M. and Al Valore for services in Italy. The Battalion was later in action at Vittorio Veneto and finished the war in Italy.Loughman was demobilised and appears in the newspapers not long after the war being fined for keeping a machine pistol as a souvenir, possibly something he picked up on a trench raid; sold together with copied research.…
'The C.O., Michael, and John had each destroyed an Me. 110, while Mac [McArthur] shot down two Junkers 87 dive-bombers. He would have got an Me. 110 also and got his sights on it, but nothing happened when he pressed his trigger. His ammunition was finished. So a very lucky Me. 110 lived to fight another day. Mac was very pleased about this fight, and certainly a bag of two for one's first action is very good. But it made him rather over-confident, and for the next few days he regarded the German Air Force rather as an organization which provided him with a little target practice and general harmless amusement. He soon learnt better!'One of numerous references to J. H. G. 'Butch' McArthur in David Crooks's wartime account of No. 609 Squadron in the Battle of Britain; Spitfire Pilot, refers.The outstanding Battle of Britain ace's immediate D.F.C. group of seven awarded to Wing Commander J. H. G. 'Butch' McArthur, Royal Canadian Air Force, late Royal Air ForceA superb airman, who had honed his flying skills in the Experimental Section of the Royal Aircraft Establishment in the lead up to hostilities, he claimed 8 confirmed 'kills' and 3 'probables' as a Flight Commander in Spitfires of No. 609 (West Riding) Squadron at the height of the Battle, on one occasion closing the range to just 10-20 yardsHis numerous combats, and those of his fellow pilots in 609 Squadron, are vividly recounted in the pages Flight Lieutenant D. M. Crook's famous wartime publication Spitfire PilotPost-war, and having served in the Royal Canadian Air Force at the time of the Korean conflict, his remarkable flying career ended in tragedy during a pleasure flight over Las Vegas in May 1961: both he and his passenger - a croupier from the famous Horseshoe Club - were killed when their aircraft inexplicably dived into the groundDistinguished Flying Cross, G.VI.R., the reverse officially dated '1940'; 1939-45 Star, clasp, Battle of Britain; Air Crew Europe Star; Defence and War Medals 1939-45; U.N. Korea 1950-54 (30386 McArthur J. H. G.), officially inscribed Canadian issue; Canadian Forces Decoration, G.VI.R., 2nd issue, the reverse of the suspension bar officially inscribed 'F/L J. H. G. McArthur', mounted as worn, good very fine (7)Provenance:Sotheby's, 6 March 1986 (Lot 628), when sold by the recipient's sister.D.F.C. London Gazette 22 October 1940:'This officer has led his flight and squadron with skill and determination. His brilliant leadership has been reflected in the high standard of morale in the flight. He has destroyed at least seven aircraft.'The original recommendation, for an immediate award which was approved by Dowding, states:'This officer has been a great asset to the Squadron since he joined it on 1 August 1940. His flying has been of the highest standard and he always leads his flight with skill and determination. On the occasions that he has led the Squadron he has displayed a sound sense of leadership and initiative. Individually he has always been keen and energetic in his desire to engage the enemy.To date he has destroyed 7 (confirmed) and 2 (unconfirmed) enemy aircraft and has severely damaged 2 others.'Covering remarks:'An outstanding fighter pilot who has now destroyed 8 enemy aircraft (confirmed) and 3 others probably, besides damaging a further 2.His brilliant and inspiring leadership has raised the morale of his flight to a very high standard since he took it over.'James Henry Gordon McArthur - or "Butch" to his friends and comrades - was born in Tynemouth on 12 February 1913 and was educated at West Jesmond Council School and Rutherford College, prior to attending the Marine School in South Shields. He subsequently found employment with the Marconi Company as a seagoing Radio Officer, in addition to obtaining certificates for Aircraft Radio Operation and Navigation.The latter qualifications led to his participation in the England to Australia 'MacRobertson Air Race' in 1934, when he flew with Captain Neville Stack, A.F.C., as his Radio-Navigator but their attempt ended in Athens - under controversial circumstances.On his return home, McArthur qualified for his Aero Certificate (No. 12614) at Redhill Aero Club in March 1935 and then teamed up with Captain T. Campbell-Black for an attempt on the London to Cape Town return record. Having flown non-stop from Hatfield to Cairo in their De Havilland Comet G-ADEF 'Boomerang', they took off for another refuelling stop in Kenya but, due to a problem with the aircraft, they were compelled to bale out north of Khartoum. Both landed safely in the desert and, on being rescued, gained membership of the famous Caterpillar Club, McArthur then being the youngest member.Brief employment as a First Officer in British Continental Airways having followed, McArthur was granted a short service commission in the Royal Air Force in May 1936. Confirmed in the rank of Pilot Officer after attending a course at R.A.F. Thornaby, he was posted to the Station Flight at Aldergrove and thence, in May 1938 to the Experimental Section at the Royal Aircraft Establishment at Farnborough as a Flying Officer and test pilot.McArthur was likewise employed on the outbreak of hostilities in September 1939 and, on being advanced to Flight Lieutenant, attended a refresher course at No. 7 O.T.U., Hawarden in July 1940. A subsequent posting to No. 238 Squadron was short-lived, however, for he was called back to Farnborough. But he continued to press for an operational posting.Battle of BritainThat wish was granted on 1 August 1940, when McArthur joined No. 609 (West Riding) Squadron, an Auxiliary Air Force unit, as a Flight Commander at Middle Wallop. Commanded by Squadron Leader H. S. Darley, D.S.O., 609 was largely manned by a pre-war class of weekend gentlemen fliers, among them Noel "Aggy" Agazarian and John Dundas; the latter's brother, Hugh, flew as wingman to Douglas Bader throughout the Battle.Over the coming weeks, on being 'scrambled' out of Middle Wallop and the satellite airfield at Warmwell, McArthur's 'brilliant leadership' of his flight - and on occasion the squadron - undoubtedly left its mark on such men. In writing to his mother in October 1940, John Dundas reported with pride that 609 was finally gaining recognition, listing McArthur's award of the D.F.C. as a case in point. He also noted that he had been given command of 'B' Flight, owing to McArthur being in hospital. More on that, later.Meanwhile, McArthur opened his operational account on 8 August 1940, when he destroyed a brace of Ju. 87s in a dogfight over the Isle of Wight-Weymouth sector. His combat report takes up the story:'…I dived on the outside of the Ju. 87 from just over 5,000 feet, fired a 7 second burst and saw him turn on his back and go into the sea. The formation then split up and I regained 4,000 feet very quickly. Height of Ju. was about 100 feet. I then dived again and gave a long burst of 10 seconds on another Ju. 87 which started to emit black smoke and dive into the sea. I then found the Me. 110. I climbed up a bit and was coming in at him from the port side and slightly above him. I turned quickly away from him and after a turn or two found myself quickly on his tail. I then found I had no more ammunition so pulled the override and hurried home … 'In Spitfire Pilot, David Crook recalls the squadron's 'bag' thus:'The C.O., Michael, and John had each destroyed an Me. 110, while Mac [McArthur] shot down two Junkers 87 dive-bombers. He would have got an Me. 110 also and got his sights on it, but nothing happened when he pressed his trigger. His ammunition was finished. So a very lucky Me. …
Army Pay DepartmentSouth Africa 1877-79, 1 clasp, 1877-8 (Capt: T. W. Drage. A.P.D.), very fine40 Medals issued to the Army Pay Department, 8 of these with clasp '1877-8'.[C.B.] London Gazette 25 June 1897.Thomas William Drage was born at Windsor on 18 October 1847 and initially served in the 17th Foot as an Ensign, selling his commission for £450 in July 1867 to take up his position as a Deputy Assistant-Superintendent of Stores. He was made Assistant-Paymaster in April 1878 and having served in Zululand (Medal & clasp), saw further campaign service in Egypt & Sudan (Medal & clasp, Bronze Star), being 'mentioned' for his services. He afterwards took up post in Barbados and retired as Colonel in November 1887, having been Chief Paymaster. He was on the Staff of His Royal Highness The Field Marshal Commanding for the 1902 Coronation (Medal).…
A good immediate 'Tobruk 1941' M.M. group of six awarded to Corporal G. Guthrie, 2nd Battalion, York and Lancaster Regiment, for his conspicuous gallantry in commanding a mortar detachment in a Bren Carrier during the capture of 'Dalby Square' on 23 November 1941 during Operation CrusaderHe subsequently served in Orde Wingate's Second Chindit Expedition, Operation Thursday, in 1944Military Medal, G.VI.R. (4745714 Cpl G. Guthrie Y.& L.R.); 1939-45 Star; Africa Star; Burma Star; Defence and War Medals 1939-45, good very fine and better (6)M.M. London Gazette 24 February 1942, the original recommendation states:'On 23 November 1941, during operations outside Tobruk, Corporal Guthrie was commanding a Mortar detachment in a Bren Carrier supporting the attack by a rifle Company on an enemy post, when about 500 yards from the objective the company came under very heavy Machine Gun and Mortar Fire. The Carrier was turned sideways to enable the mortar to come into action behind it; whereupon it immediately came under heavy and accurate Machine Gun Fire. In spite of this Corporal Guthrie immediately proceeded to unload the mortar and ammunition himself and got his mortar into action. When short of bombs he made several journeys to the enemy side of the carrier to obtain more bombs although the enemy fire had not been subdued. During the whole operation Corporal Guthrie maintained his mortar in action and by his coolness and disregard of the enemy fire set an excellent example to the men under his command.'The recommendation was additionally endorsed by the Brigadier Commanding 14th Infantry Brigade:'Recommended for an immediate award of the Military Medal for conspicuous gallantry and devotion to duty under fire.'George Guthrie was a native of Leeds, a mill worker at Pool, Lorrimer and Tabbener's prior to the war. He attested as a regular soldier in the York and Lancaster Regiment and served with the 2nd Battalion during the Second World War initially in North Africa. Awarded the M.M. for his gallantry on 23 November 1941, he was with 'B' Company, 2nd Battalion, under Captain Northover when he was given the task of capturing 'Dalby Square', a large enemy post on the western side of Tobruk:'The attack was across flat country devoid of cover. The enemy put up a very strong resistance. He was holding his post with a large number of machine guns and light automatics, which his defensive artillery fire was intense and accurate. About 400 yards from the objective "B" Company was held up. Two Bren carriers with 3-inch mortars were then brought forward, and using the carriers as cover, both detachments opened up on the enemy. This had the immediate effect of reducing the enemy's small-arms fire. "B" Company then advanced again and rushed the position with the bayonet.' (The Regimental History refers).After serving in the Western Desert, Guthrie proceeded to India and saw further service with the 2nd Battalion as part of Orde Wingate's second Chindit Expedition, Operation Thursday, in early 1944 where the 2nd Battalion, York and Lancaster Regiment was part of 65 and 84 Columns; sold together with copied research.…
Six: Major L. F. Scott, Oxfordshire and Buckinghamshire Light Infantry, late North Nigeria Regiment, who served as A.D.C. to Sir George Chardin Denton in Lagos and later A.D.C. to the Governor of GambiaEast and West Africa 1887-1900, 1 clasp, 1897-98 (Lieut. L. F. Scott. N. Nigeria R.); Queen’s South Africa 1899-1902, 4 clasps, Relief of Kimberley, Paardeberg, Driefontein, Transvaal (Capt. L. F. Scott. Oxford. L.I.), rank corrected; King’s South Africa 1901-02, 2 clasps, South Africa 1901, South Africa 1902 (Capt. L. F. Scott. Oxford L.I.); 1914-15 Star (Capt. L. F. Scott. Oxf. & Bucks. L.I.); British War and Victory Medals (Capt. L. F. Scott.), good very fine (6)Lionel Folliott Scott was born at Arlesley, Bedfordshire, on 23 October 1870 the son of the Reverend Richard Scott of Bennett's Farm, Arlesley and his wife Emily. He attended Repton School and joined the 3rd (Militia) Battalion, Suffolk Regiment. From there he was commissioned Lieutenant on 26 April 1893 with the Oxfordshire & Buckinghamshire Light Infantry.Advanced Lieutenant with them in 1897, he saw service with the West African Field Force in the Lagos Hinterland. In the aftermath of prolonged wars between the mainland Yoruba states, the Lagos Colony established a protectorate over most of Yorubaland between 1890 and 1897. Lagos Colony was a British colonial possession centred on the port of Lagos in what is now Southern Nigeria. Lagos was annexed in August 1861 and declared a colony on 5 March 1862.Sir George Chardin Denton K.C.M.G., Colonial Secretary of Lagos and in 1900 was appointed Governor and Commander-in-Chief, who was in office from 1900 until 1911. Scott was appointed his Aide-de-Camp, attached to the North Nigeria Regiment for a period between 1897-8.Returning to his Regiment he saw service with the 1st Battalion Oxfordshire Light Infantry throughout the Second Boer War. As a Special Service Officer he served in the Relief of Kimberley; operations in the Orange Free State, February-May 1900, including service at Paardeberg; Poplar Grove and Driefontein; and operations in the Orange River Colony, May 1900-May 1902.An article in the Bucks Herald on 24 November 1900 states:'Lieutenant Lionel Scott has been promoted to the rank of Captain in the Oxfordshire Light Infantry, in succession to Major Fairtlough, who is Adjutant of the Bucks Militia Battalion. Captain Scott commenced his career in the old West Suffolk Militia, and has for some time past been employed in South Africa as a Special Service Officer.'Still in Africa after the war he was appointed A.D.C. to the Governor and Commander-in-Chief of Gambia in 1902, serving there until 1906. His replacement in the role was a man by the name of Edward Kirkpatrick whom Scott befriended, he was later to marry his sister Florence.Becoming the Adjutant of the Special Reserve Battalion in 1908 Scott served in that role for some time before retiring in October 1912. He joined the Reserve of Officers and as such was recalled to service in the Great War, being placed in command of 'D' Company, 2nd Battalion Oxfordshire & Buckinghamshire Light Infantry on 13 December 1914.Initially serving as Railway Transport Officer in Britian he later entered the France on 7 December 1915. Tragically his brother-in-law Captain Kirkpatrick was killed in action in 1915. Scott served at the front until February 1917, being appointed Regimental Transport Officer alongside his other duties. He returned to Britian and served as a Major in the Labour Corps. He died at Quarry House, Headington, Oxford on 7 January 1941; sold together with copied service papers.…
The 1960 C.B.E. group of four to Captain W. R. J. Redman, Royal Navy, who pre-war served as a Gunnery Specialist and later served as a member of the Ordnance Board and eventually became Chief Inspector of Naval OrdnanceThe Most Excellent Order of the British Empire, Military Division, Commander's (C.B.E.) neck Badge, silver-gilt and enamel; Defence and War Medals 1939-1945; Coronation 1953, the campaign medals mounted as worn, very fine or better (4)C.B.E. London Gazette 31 December 1960.William Richard Jeffries Redman was born on 27 October 1905 and joined the Royal Navy in September 1923 as a Naval Cadet (Special Entry). Promoted to Midshipman in 1924, he served on Royal Sovereign and Versatile and then went to the Royal Naval College at Greenwich in December 1926. Redman was promoted Lieutenant in 1928 and saw service on Venomous, Verity, Pembroke and Tiverton. In September 1931 he saw service at the Royal Naval College at Greenwich and later served at Excellent and carried out a qualifying course for specialism in Gunnery.He became an Instructor of Gunnery at the Royal Naval Gunnery School based at Chatham in July 1934 and, after a brief spell on Cairo, served at the Naval Ordnance Inspectorate at Woolwich as Assistant Inspector of Naval Ordnance and during his time there was promoted to Lieutenant Commander. By March 1940 he was based at Headquarters Chief Inspector of Naval Ordnance as Assistant to the Chief of Naval Ordnance and had reached the rank of Commander. In November 1943 he served at the Proof and Experimental Establishment based at Pendine, South-West Wales and served as the Deputy Superintendent.After the war, he served at the Proof and Experimental Establishment this time based at Inchterf as Deputy Superintendent in Charge before being sent to the Naval Ordnance Department Headquarters at Bath in June 1948 where he served as Assistant to the Director of Naval Ordnance. By November 1954 he was serving with the Ordnance Board having the responsibility for the Board's work on guns for all services (this shared with the Army). Redman was attached to the Chief Inspector of Naval Ordnance in June 1958 with the position of Deputy C.I.N.O. and became Chief Inspector in February 1962 a position he held until April 1966. He became Captain (Retired) and was re-employed as Naval Ordnance Inspecting Officer Group B, based at the Royal Ordnance Factory at Glascoed, South-East Wales, a position he held until August 1968. Redman later died at Bath in 1971.Sold together with an archive comprising:(i)Certificate for the C.B.E. in Central Chancery envelope.(ii)Garrard & Co. Ltd. case of issue for the C.B.E.(iii)Certificate for the Coronation 1953 medal.(iv)Officers Training Corps Certificate, Dover College dated "A" 18 July 1923.(v)Warrant for Promotion to Sub-Lieutenant dated 28 February 1928.(vi)Certificate for Instruction in Gunnery dated 30 September 1932.(vii)Results of Examinations Lieutenants "G" Qualifying 1932.(viii)Certificate for Member of the Institution of Engineering Inspection, dated 14 October 1959.(ix)Book: A History of the Order of the British Empire.(x)Statutes of the Most Excellent Order of the British Empire 1957.(xi)Service of Dedication in St. Paul's Cathedral to celebrate the Jubilee of the Order, dated 24 May 1967.(xii)A large amount of correspondence to include details relating to his Investiture, numerous letters of congratulation from both Military and Civilian.(xiii)A large number of photographs, both professionally and amateurly shot to include one taken outside Buckingham Palace after his Investiture, together with a family album of photographs.(ix)A prize medal from H.M.S. Royal Sovereign (Arbuthnot Trophy Race. 1924. 8th Man Home.).(x)A copy of his record of service.A photocopy of the Official History of the Department of the Chief Inspector of Naval Ordnance.(xi)A quantity of assorted letters to his wife, housed in an attache case.(xii)A brass door plaque named (W. R. J. Redman R.N. No 1.)For his miniature dress Medals, please see Lot 444.…
90th Regiment of Foot (Perthshire Volunteers)The Regiment embarked from India on the Nubian with the war correspondent Melton Prior for the Cape Colony in January 1878 and fought in the 9th Xhosa War later that year. It also saw action at the Battle of Kambula & Ulundi during the Anglo-Zulu War and returned for India in October 1879.1,021 Medals to the unit, 66 of these with clasp '1877-8'.South Africa 1877-79, 1 clasp, 1877-8 (1611. Pte. W. Heridge. 90th. Foot.), very fine…
Canada General Service 1866-70, 1 clasp, Fenian Raid 1866 (Pte. W. Hempstock 13th. Bn.), rivet a little proud to reverse, good very fineWilliam Hempstock is confirmed upon the Medal Roll as being present at 'Ridgeway & Port Colbourne' with the 13th Battalion, now the Royal Hamilton Light Infantry.The unit were present at the Battle of Ridgeway on 2 June 1866 and saw action against the Fenian Brotherhood under the command of Brigadier-General John O'Neill. The 13th Battalion saw 15 men wounded in the action.…
The Great War M.M. awarded to Lance Corporal T. Glancey, 1/8th Battalion, Argyll & Sutherland Highlanders (Territorial Force), pre-war territorial with the 9th (Dumbartonshire) Battalion he managed to survive the terrible losses at the Second Battle of Ypres which saw that Battalion amalgamatedMilitary Medal, G.V.R. (302866 L.Cpl. T. Glancey. 1/8 A.&S. Hdrs - T.F.), light pitting and contact wear overall, very fineProvenance:Spink, December 1977.M.M. London Gazette 11 May 1917.Thomas Glancey was born at Cardross, Dunbartonshire, Scotland and attested with the 9th (Dumbartonshire) Battalion, Argyll & Sutherland Highlanders in 1911, serving with them as a Territorial. He was embodied for service on 5 August 1914 with the 1/9th Battalion, joining them in France on 19 February 1915. Going into action at the Second Battle of Ypres the 1/9th Battalion suffered appalling losses between 10-18 May. They lost 12 officers and 300 men on the first day alone, in effect they ceased to exist as a fighting unit, being temporarily amalgamated the 7th Battalion but were never brought back to strength.Glancey did not remain with the Battalion, returning to Britian on 1 June 1915 and remaining there until 6 August 1916. Shortly after his return he was posted to the 1/8th Battalion in October. This unit was stationed around the Somme at the time at soon went into action in the Capture of Beaumont-Hamel.The Battalion saw further heavy action at Arras and Cambrai in 1917, then transferring to the 61st (2nd South Midland) Division in February 1918. Glancey remained with the Battalion until the end of the war, being demobilised on 31 March 1920. After demobilisation he returned to the Reserves and continued to serve with the 9th (Dumbartonshire) Battalion, being finally discharged on 3 February 1930.…
Sold by Order of a Direct DescendantThe outstanding Czech War Cross & Czech Bravery Medal group of ten awarded to Flight Lieutenant A. Vrana, Royal Air Force, late Czech Air Force and French Foreign Legion l'Armee de l'Air Groupe de Chasse 1/5Vrana had the admirable record of one kill and two probables during the Battle of France, having then transferred to Britain, he flew in the Hurricanes of No. 312 (Czechoslovak) Squadron during the Battle of Britain as just one of just 88 Czech Pilots1939-45 Star, clasp, Battle of Britain; Air Crew Europe Star; War Medal 1939-45; General Service 1918-62, 1 clasp, Cyprus (Flt. Lt. A. Vrana. R.A.F.); France, Republic, Legion of Honour, silver and enamel; Croix de Guerre, reverse dated '1939', with Palme upon riband; Czechoslovakia, Republic, Czechoslovak War Cross 1939, with three further Award Bars; Bravery Medal, with Second Award Bar; Military Merit Medal, silver; Army Commemorative Medal, 1st Type, mounted court-style as worn by Spink & Son, St James's, London, good very fine (10)Adolf Vrana - or Ada to his friends and comrades - was born at Nová Paka, Bohemia in October 1907. Having come of age, Vrana undertook his national military service and joined the Czechoslovak Air Force. First in the ground crew at Prague-Kbely and Hradec Králove fields, he was then selected for Pilot training. Vrana passed though in 1931 and was assigned to the 41st Fighter Squadron as a fighter pilot.He further gained skill in night flying, observation and also qualified on seaplanes, going to the Hranice Military Academy in 1934. Made Pilot Officer in 1936, he was with the 91st Squadron, at that time the only night fighter Squadron. Vrana thence trained as an instructor and a test pilot.Following the Nazi occupation of Czechoslovakia in March 1939, all its personnel found themselves without employment. Thus Varan and many of his colleagues made a break for it, arriving to the Consulate in Krakow some months later. The plan would be to make for Franch, which was completed via a coastal cruiser that took him to Calais.The French Foreign Legion was the option open, with the understanding that should a Second World War be declared, those in the service would then join Regular French Units. Some who had joined were fortunate to be transferred onto the most usual postings in Africa which were commonplace with the Foreign Legion, Vrana was still in France when War was declared. He was duly released to the l'Armée d'Air and went out to Chartres air field.Battle of France - first bloodHaving undergone familiarisation with the French systems and aircraft, Vrana operated the Curtiss Hawk 75 from Suippes, near Rheims with the Groupe de Chasse 1/5.The Battle of France saw Allied airmen gain significant experience in aerial combat, which would come to the fore in a few short months. Vrana wasn't to know that at the time, for they were regularly 'scrambled' to action on multiple occasions. Of his own record, Vrana was shot down on 13 May 1940 by a Me109, his life being saved by parachute after having bailed out. He shared in the destruction of a He111 on 26 May 1940 and shared in the probable destruction of a Hs126 and a He111 on 7 June 1940. As the German advance came on apace, the Group found itself moving to safety on numerous occasions.After the French collapse, Vrana and other Czechs flew their Hawks from Clermont-Ferrand to Algiers on 17 June. They made their way to Oran, at that point learning that France had fallen. Whilst at that place, together with four other gallant airman, Vrana was presented with his two French awards for his gallantry during the previous period of action. They then went to Casablanca, from where they went by boat to Gibraltar, where they joined a convoy bound for Britain, answering the call of Churchill that they would be welcomed to Britain to continue the fight.Battle of BritainProcessed into the Royal Air Force, he joined No. 312 (Czechoslovak) Squadron at its formation at Duxford on 29 August 1940. They were to be equipped with Hurricane Mark I's. They moved to Speke in September as part of the defence of Liverpool and her precious docks.Of his Ops with No. 312 Squadron, the Operational Record Books provide the following, all 'Scrambles':21 October - P3810 1135hrs.22 October - P3810 1620hrs.24 October - V6810 1310hrs.22 November - V6926 1040hrs.26 November - V6926 1155hrs.27 November - V6926 1625hrs.28 November - P3612 1250hrs.5 December - P3759 1120hrs.Further flightsBesides this, Vrana then assisted in transferring four of their aircraft on 8 December and would have been back in time for the visit of the Czech President on 17 December, who toured the Squadron and met the Pilots. At the end of his operational tour in April 1941, Vrana was posted to 3 ADF at Hawarden. Variously serving with No. 310 Squadron at Martlesham Heath in the Operations Room as a Flight Control Officer, he returned to No. 312 Squadron for a further Operational Tour in June 1942. Tour expired the following year, Vrana then went to serve at the Czechoslovak Inspectorate General and as Czechoslovak Liaison Officer at HQ Fighter Command, Bentley Priory.Returned to his homeland at the end of the conflict, he learned that his parents were lucky indeed to have survived time in a Concentration Camp. He rejoined the Czech Air Force when it was being rebuild and became Commanding Officer of the Research Institute and Testing Unit. His Czechoslovak War Cross 1939 with Three Bars followed in September 1945, being promoted to Lieutenant-Colonel and Commander at Prague-Kbely field. When the communists took over in February 1948, he saw the way in which those who had served the Allied forces treated. It was clearly not a risk he wanted to take and Vrana escaped with his wife. Having been granted leave from the Air Force, he made it across to West Germany in late 1949. Vrana once again returned to the United Kingdom and rejoined the Royal Air Force. Having seen further campaign service in Cyprus (Medal & clasp), he retired Flight Lieutenant in May 1961. Granted the rank of Colonel in the Czechoslovak Air Force, he died in Wiltshire on 25 February 1997.His name is recorded on the National Battle of Britain Memorial and the London Battle of Britain Memorial, besides a memorial plaque in his home town and upon the Winged Lion Monument at Klárov, Prague.Sold together with an impressive archive of original material comprising:i) His riband bar, removed from his uniform, with gilt rosette upon 1939-45 Star denoting 'Battle of Britain'.ii) His R.A.F. Pilot's 'Wings'.iii) Czech Air Force Epaulettes.iv) Czech Pilot's dagger, marked 'Wlaszlovits, Stos', brass hilt with inlay, brass and leather scabbard, the blade of steel.v) Croix de Guerre aiguillette.vi) Data plate removed from an aircraft, marked 'Curtiss H75A-1 No. 43 1-39'.vii) Czech Pilot's Badge, by V. Pistoira, Paris, 1940, a rare award of French manufacture, numbered to the reverse 'F121'.With thanks to Simon Muggleton for accessing the ORB's.Subject to 20% VAT on Buyer’s Premium. For more information please view Terms and Conditions for Buyers.SALE 25001 NOTICE:'Now offered together with his French Pilot's Badge, this officially numbered '33644', photographs available via SpinkLIVE.'
The Second World War period K.P.M. pair awarded to Inspector G. Campbell, New South Wales Police ForceKing's Police and Fire Services Medal, for Distinguished Service, G.VI.R., 1st issue (G. Campbell, Inspr., N.S.W.P.F.); Jubilee 1935, good very fine (2)K.P.M. London Gazette 11 June 1942.George Campbell was born in New South Wales on 16 March 1880 and saw active service as a Gunner in 'A' Battery of the Royal Australian Artillery in the Boer War.Described as being 6 ft. tall and weighing 13 stone on his enlistment in the N.S.W. Police Force in July 1903, he was posted as a Constable to the Eastern District but later served in Double Bay. His subsequent promotions were to Sergeant 3rd Class in October 1922, 2nd Class in January 1929 and 1st Class in July 1933, followed by his appointment to Inspector in April 1937.Campbell retired in March 1941, shortly before the announcement of his award of the K.P.M., and he died in July 1965; sold with copied service record and verification for the Jubilee 1935 Medal.…
'H.M.S. Eclipse was escorting a Northern convoy on 29th March 1942 when in Arctic weather she fought an action with German destroyers of the Narvik class. In a running fight in the snow she badly damaged one of the enemy, hitting her six times with 4.7 shells. As the Eclipse was about to finish off this ship with a torpedo attack two other German destroyers appeared, and the Eclipse was hit. She hit one of the enemy, which did not pursue them, and she proceeded to Murmansk. She had been handled throughout with great skill and determination in very severe conditions, with one of her guns out of action owing to ice.'(The remarkably exciting award recommendation for Eclipse's crew following her life and death struggle in Artic Waters)An exciting Post-War C.V.O. group of nine awarded to Commander D. L. Cobb, Royal Navy, who was 'mentioned' as gunnery officer of Eclipse during a remarkable destroyer action in March 1942 which saw her cripple a German destroyer only to be engaged by two more enemy vessels and drive them offLater 'mentioned' again for good service in the Aegean including his bravery in the tragic sinking of Eclipse, Cobb went on to command Cockade when she brought relief to those affected by the 1957 Sri Lankan Floods and was heavily involved in implementing the Duke of Edinburgh's Award while a Deputy LieutenantThe Royal Victorian Order, Commander's (C.V.O.) neck Badge, silver and enamel, in its Collingwood box of issue; 1939-45 Star; Atlantic Star; Africa Star; Italy Star; War Medal 1939-45, with M.I.D. oak leaf; Korea 1950-53 (Lt Cdr. D. L. Cobb R.N.), officially re-impressed; U.N. Korea 1950-54; Jubilee 1977, the last eight mounted court-style as worn, overall very fine (9)C.V.O. London Gazette 31 December 1977.David Laurence Cobb was born in March 1922 in Hendon, London, the son of Samuel and Mary Cobb. He joined the Royal Navy as a Naval Cadet on 1 May 1939 and was advanced Sub-Lieutenant during the Second World War. Posted to H.M.S. Eclipse he was 'mentioned' for his services during a convoy escort mission with her (London Gazette 23 June 1942). The award recommendation includes greater detail stating:'As Gunnery Control Officer, controlled a steady and accurate fire on the enemy, hitting him repeatedly, under very difficult conditions.'Still with her when she was transferred to the Aegean, Cobb received further plaudits for his cool and effective gunnery. This gunnery was put to the test during the Gaetano Donizetti action on 22 September 1943. This Italian freighter had been seized by the Germans to carry arms to Rhodes, escorted by the torpedo boat TA10. Eclipse encountered the convoy and attacked immediately, her guns were worked immaculately, sinking Gaetano Donizetti in minutes and damaging TA10 so heavily that she was scuttled days later.Cobb was again 'mentioned' for 'Operations in Dodecanese Islands culminating in the sinking of Eclipse on 24 October 1943' (London Gazette 4 April 1944 refers). The recommendation adds:'A painstaking and efficient G.C.O., always cheerfull [SIC] in adversity and setting a high example. His handling of the gun armaments was responsible for the successful outcome of two engagements in the Dodecanese against surface craft.'Still with her the next month Cobb was present for the horrific sinking of Eclipse, when she struck a mine on 24 October and broke in two, sinking within five minutes. Of the ships complement of 145 men there were only 36 survivors and tragically at the time she was also carrying 'A' Company, 4th Battalion, Buffs (Royal East Kent Regiment), who lost 134 men out of 170.Cobb was extremely lucky to survive the sinking and joined the complement of Beaufort on 18 December 1943. This vessel was stationed in the Aegean as well and was present for the bombardment of Kos and later the failed attempt to halt the German invasion of Leros.Post war Cobb continued to serve being promoted to Lieutenant Commander on 16 February 1950 and later Commander in 1953. Posted to command H.M.S. Cockade in 1957, taking part in relief efforts of the Sri-Lankan Floods of 1958. That same year Cobb took part in the Navy Pageant at the Royal Tournament.Placed upon the retired list on 2 January 1961 and was appointed assistant secretary of the Duke of Edinburgh Award scheme. Appointed Deputy Director of the Duke of Edinburgh Award scheme in 1977 and the same year Deputy Lieutenant of Greater London. It was likely for his work with the Duke of Edinburgh Awards that he was awarded his C.V.O.. Cobb died at Sydney, Australia on 29 January 1999; sold together with copied research.…
The Indian Mutiny Medal awarded to Able Seaman J. Kennedy, Royal Navy, one of Captain Peel's famed 'Shannons'Indian Mutiny 1857-59, 1 clasp, Lucknow (Jas Kennedy, A.B. H.M.S. Shannon), suspension somewhat slack, light contact marks, very fineJames Kennedy served with H.M.S. Shannon with the number 344 and appears as a Leading Seaman on the roll. The Shannon was an imposing Liffey-class steam frigate armed with 51 guns. Originally intended for service in China, she left Hong Kong in company with the Pearl when news broke of the Indian Mutiny. When she docked at Calcutta in August 1857 she was, at that time, the largest vessel to have navigated so far up the River Hooghly. Her Captain William Peel V.C., C.B., took a considerable risk in moving her into such shallow water, but subsequent events were to prove him a man undaunted by any danger.Sir Patrick Grant, who was then acting Commander-in-Chief at Calcutta, knew that British forces in Oudh were woefully short of heavy guns. He ordered Peel to form a Naval Brigade comprising 'Bluejackets' from both the Shannon and the Pearl. The contingent from Pearl numbered 175 men, bringing the Naval Brigade's total strength to 408 officers and men, including Marines from both ships.This force was armed with: ten 8-inch 68-pounders with 400 rounds of shot and shell per gun, four 24-pounders, four 12-pounders, a 24-pounder howitzer, and eight rocket tubes. 800 bullocks were required. For the voyage up the Ganges, the men and guns were to be transported in a steamer called the Chunar, as well as a flat-bottomed transport. The force left Calcutta on 29 September, heading straight towards 'The Devil's Wind'.On 10 October, the contingent from Pearl stopped at Buxar on the Ganges, and thenceforward operated separately under the command of Captain E. S. Sotheby. The remainder of Peel's Naval Brigade, already nicknamed 'The Shannons', continued up the Ganges to Cawnpore, where British forces were gathering for the Second Relief of Lucknow. Peel kept the men occupied with constant drilling and manoeuvres. He knew that in battle, the guns would have to be moved using drag ropes, eighteen men to each gun.Sir Colin Campbell was greeted with a great cheer when he arrived at Cawnpore on 31 October, assuming command of the army. His force only amounted to 3,400 men, made up of detachments from HM 8th, 23rd, 53rd, 82nd, 90th and 93rd Foot, the 2nd and 4th Punjab Infantry, and the 9th Lancers. Peel's Naval Brigade thus proved invaluable when the force arrived before Lucknow on 15 November.The next day, Peel's guns and two heavy guns of the Royal Artillery began a fierce bombardment of the Sikanderabagh, a huge rebel-held building, 130 yards square, with a thick, brick, loopholed wall 20 feet high, flanked by bastions at the corners. After firing for 90 minutes, the guns had created a small hole, three feet high and three and a half feet wide. As their pipers struck up the Highland Charge 'Haughs of Cromdale', men of the 93rd Highlanders surged forward in the hope of being the first to enter this 'breach', and won six Victoria Crosses.Although losses at the Sikanderabagh were severe, the stormers were able to trap about 2,000 mutineers in a corner of the building. Remembering earlier atrocities, particularly the massacre of women and children at Bibighar, Cawnpore on 15 July (the gore at Bibighar lay undisturbed, creating a nightmarish scene for troops passing through), the stormers killed every man they found. Lord Roberts later recalled:'There they lay, in a heap as high as my head, a heaving, surging mass of dead and dying inextricably tangled.'The capture of the Sikanderabagh enabled Campbell's army to reach the beleaguered Residency compound, but having lost 45 officers and 496 men, Campbell realised he could not possibly hold Lucknow against the vast rebel armies in the region.On 19 November, the evacuation of the Residency began. Women and children who for six months had suffered unimaginable terrors emerged from its shattered ramparts and filed towards Dilkushah, under the protection of the 9th Lancers. Campbell organised the evacuation so that the enemy never suspected a British withdrawal. The Naval Brigade was pivotal to this conceit: while Peel's guns and rockets pounded the Kaiserbagh as if in preparation for an assault, women and children were silently extricated from the Residency compound, under the noses of a distracted foe. Part of the rearguard, Peel's Bluejackets were among the last to quit Lucknow on the night of 22 November; it was many hours before the mutineers realised that the Residency was empty.Return to CawnporeJust before leaving Cawnpore for Lucknow, Sir Colin Campbell had left 500 men to defend the city under the command of General Windham. Included in this garrison were fifty Bluejackets of the Shannon, with two 24-pounders, led by Lieutenant Hay and Naval Cadets Watson and Lascelles. Cawnpore lay on the Grand Trunk Road, its bridge of boats over the Ganges a vital artery for British supply and communication. Most of Campbell's reinforcements arrived via Cawnpore (hence why the massacre there had such impact).On 19 November, Windham's tiny garrison was invested by 25,000 mutinous sepoys of the Gwalior Contingent, led by Tantia Tope. Windham's men, including the Bluejackets, dug entrenchments at each end of the bridge of boats and managed to hold it for ten days. Since Kennedy was not awarded the 'Relief of Lucknow' clasp, he may very well have been a part of this 50-strong detachment at Cawnpore.Hearing of Windham's plight, Campbell left Sir James Outram with a small force to hold the Alum Bagh, near Lucknow. With the remainder of his army, including the Naval Brigade, Campbell dashed southwards. When heavy gun-fire could be heard from Cawnpore on 27 September, Campbell pressed ahead with his cavalry and horse artillery. He linked up with Windham's entrenchments the following day, and to his great relief, the bridge of boats remained intact.The Naval Brigade arrived on the northern bank of the Ganges two days later. The mutineers had massed their artillery on the southern bank, aiming to destroy the bridge of boats, but Peel's guns quickly silenced them. Over subsequent days, Campbell arranged for the sick, wounded and non-combatants from Lucknow (over 2,000 souls) to be escorted to Allahabad, thence to Calcutta. This left him free to conduct offensive operations. He received reinforcements, including a wing of the 42nd Foot, bringing his total force to 600 cavalry, 5,000 infantry and 35 guns. On 6 December, he launched a full-scale assault across the river. In The Devil's Wind: The Story of the Naval Brigade at Lucknow (1956), G. L. Verney tells how the Naval Brigade lifted morale when the assault began to falter:'Every attempt at forward movement was met by a storm of shot, shell and bullets, the slow rate of fire of the [rebel] muskets being compensated by the large number of men handling them. Each rush cost a few lives and it looked bad. In the clouds of dust and smoke which billowed across the plain, it was hard for commanders to see what was happening or why the advance in that area was making so little progress. To those in front, it seemed that increased artillery support was their only hope.Suddenly, however, the men of the 53rd Foot and the 4th Punjab Infantry, lying down near the bridge and extended short of the bank of the Canal, heard a rumble of wheels behind them, and there they saw Captain Peel, followed by a 24-pounder gun, hand-drawn and double-crewed, some forty Seamen, running hard, followed by a limber. "Action Front" shouted Peel, an…
'Dispatch Rider Posed As Italian - Gave Nazis Slip'(The Manchester Evening News 15 October 1943, refers)A superb 'Escaper's' M.M. group of seven awarded to Private J. Chatham, 2nd Battalion, Cheshire Regiment, a dispatch rider who went 'in the bag' at the Battle of the Knightsbridge Box in June 1942Held in the same camp as S.A.S legend "Gentleman Jim" Almonds, Chatham's escape appeared on the same list of recommendations as Almonds' Second Award BarChatham's journey through Italy saw him briefly re-captured while trying to board a ship, again escaping and he managed to obtain passes by pretending to be ItalianMilitary Medal, G.VI.R. (4123232 Pte. J. Chatham. Ches R.); 1939-45 Star; Africa Star; Italy Star; France and Germany Star; Defence and War Medals 1939-45, light contact marks, very fine (7)M.M. London Gazette 27 April 1944, the original recommendation states:'Both captured in Jun 1942 near Knightsbridge. Subsequently imprisoned at Capua and then Campo 70 (Monturano). After the Armistice P/W were forbidden by the Senior British Officer to attempt escape, and armed British picquets were posted to support the Italian guards. Gill and Chatham, however, escaped by getting over the outer wall and knocking out a sentry obtained civilian clothes, and made their way to Termoli. Here they were caught by Germans when boarding a ship, and locked up in a house. They escaped from here through a window at night, boarded the boat again, and so reached Istonio. They walked to Manfredonia but found they could not leave the town without passes. They went to German H.Q. and speaking Italian asked for passes to Bari, which they received. They met British troops near Andria on 23 Sep 43.'Jack Chatham was a native of Manchester and enlisted in the Cheshire Regiment, serving with the 2nd Battalion during the Second World War. They saw action at the Battle of the Knightsbridge Box starting on 10 June 1942, part of the Battle of the Gazala. Unfortunately, the Battle went poorly for the British and the Cheshire Regiment - serving with the 50th Division - were cut off, forcing them to break through an encircling cordon of Italian troops.During the chaos of the breakthrough Chatham, serving as a dispatch rider, was taken prisoner of war - listed as going in the bag on 16 June. Alongside him at the time was Private J. E. Gill who, along with many others, were taken with Chatham to Capua, after which they were transferred to Campo 70 at Monturano.Not long later another P.O.W. arrived at the camp, Sergeant (later Major) John "Gentleman Jim" Almonds, who had been captured at Benghazi on 14 September. He attempted to escape very quickly, with several companions; he distracted the Italian guards with coffee, remained longer than was allowed in the Red Cross hut and when darkness fell emerged to disable the sentry. The escape was successful however when several members of the group fell sick they had no choice but to give themselves up.In the meantime the Allied advance gained pace, Sicily fell and Italy was invaded, this in turn triggered the Italian Armistice on 3 September 1943. As Campo 70 was an Italian camp this caused some confusion and eventually the Italian Guards deserted.It was at this moment that a number of prisoners including Chatham and Gill decided to escape, they managed to get out of the camp but this was just the start of their adventures, a report on Gill's escape in The Cheshire Observer provides further detail:'They made their way down the East side of the peninsula and, to escape detection at one point took advantage of an Italian's offer to buy a rowing boat, and managed to do 50 miles by water in about 10 hours. At one stage of the journey the two men were recaptured by the Germans. They were put in a small room for the night and were told they would be dealt with in the morning. When morning came, there seemed to be no sentry about so they hopped out of the window and were on their way again!'This is added to from Private Chatham's perspective in the Manchester Evening News on 15 October 1943 which states:'He had nerve enough to "wangle" a pass to go South out if the Nazis who stopped him and his friend when they were posing as Italians, and to travel about 150 miles on foot before they "wangled" a fishing boat to finish the last 50 miles to join their comrades.'Sold together with copied research.…
58th RegimentThe 58th 'Rutlandshire' Regiment was stationed at Grand Shaft Barracks, Dover when, on 11 February 1879, it received orders to hold itself in readiness to proceed on active service to South Africa. Embarked at Portsmouth in the hired transport Russia, the men arrived at Durban on 4 April and proceeded via Pietermaritzburg and Ladysmith to Landman's Drift.Aided by the 5th Brigade R.A., the men set to work constructing Fort Whitehead at Koppie Allein. Using this fort and Fort Evelyn as staging posts, the Regiment conducted numerous reconnaissance missions and on 3 July a water picquet of the 58th was fired upon by Zulus concealed behind rocks, within a mile of the White Umvolosi. This action lasted for approximately three hours and one man was wounded.Four companies of the Regiment were engaged at the battle of Ulundi; Lance-Corporal Tomkinson was killed and 13 others wounded. In Regimental Orders dated 4 July, Colonel Whitehead congratulated the officers, non-commissioned officers, and men, on the coolness exhibited by them when under fire; General Newdigate thanked the regiment for its gallant behaviour during the action.After Ulundi the regiment commenced building Fort Victoria and returned to garrison duties.1034 Medals were issued to the 58th Regiment, 689 of them with the '1879' clasp.South Africa 1877-79, 1 clasp, 1879 (29/905 Pte. W. Alberry. 58th Foot.), suspension sometime re-affixed, heavy contact marks, fineWilliam Alberry was born at Rogate, Sussex in 1855 and was a servant by trade upon his joining the 58th Foot at London in March 1878. He served with the unit in South Africa from July 1879-February 1880 and saw further service in South Africa from February-May 1881. The unit fought at the Battle of Laing's Nek in January 1881 and the Battle of Majuba Hill in February 1881 during the First Boer War, on the former day it was the last regiment to carry its regimental colours into battle and Lieutenant Alan Richard Hill won the Victoria Cross. Alberry was discharged in October 1884.…
The Crimea Medal awarded to Private H. Turner, 41st Regiment of Foot, who was twice wounded in action before Sebastopol, the second time so severely that he was invalided from serviceCrimea 1854-56, 3 clasps, Alma, Inkermann, Sebastopol (H. Turner. 41st Foot), officially impressed naming, double struck, slight edge bruise, otherwise very fineHenry Turner was born at Barnstaple, Devon in 1818 and attested with the 41st Regiment of Foot on 25 June 1840. He served for over sixteen years, including over five abroad with two years and nine months of that spent in India. Arriving in the Crimea with the rest of the Regiment in the summer 1854, he saw action at the Battle of the Alma where the Battalion formed part of the 2nd Division, supporting the French attack on Telegraph Hill.Later taking part in the Battle of Inkermann they captured a set of Russian drums during the confused and bloody battle. Turner was twice wounded during the fighting, slightly on 21 April 1855 and then again severely later on 17 August of the same year. The second injury is likely the one referenced in his discharge papers 'a severe gunshot wound on the left thigh received while he was at Sevastopol which now renders him unfit for service.'Turner was invalided from service on 30 December 1856; sold together with copied research.… 25001 SALEROOM NOTICE:Lot is NOT subject to 5% Import Tax.
The 'Battalion of Passchendaele 1917' D.S.O, M.C. group of six awarded to Lieutenant-Colonel R. A. Rochford, Royal Warwickshire Regiment, late Royal Inniskilling Fusiliers and Grenadier Guards, awarded a field commission in 1915 he served with distinction, losing an arm in the same action which won him the D.S.O. he remarkably continued to serve and was responsible for the defence of Avonmouth docks and Filton Aerodrome during the Second World WarDistinguished Service Order, G.V.R. silver-gilt and enamel; Military Cross, G.V.R., unnamed as issued; 1914 Star, with clasp (13664 Sjt: R. A. Rochfort. 1/G.Gds:); British War and Victory Medals (Capt. R. A. Rochfort.), with M.I.D. oak leaves; War Medal 1939-45, mounted as worn, nearly extremely fine (6)D.S.O. London Gazette 15 April 1915, the original citation states:'For conspicuous gallantry and devotion to duty. When the Battalion, on its way up to the line, was heavily bombarded with gas and other shells and was in danger of losing its way in the gas masks in the darkness, he placed himself at the head and guided it to its forming -up place in time. Although severely wounded the following day while leading his men, he remained with them for nearly two hours, until forced to desist through sheer exhaustion. He showed splendid determination and resource.'M.C. London Gazette 17 April 1917.M.I.D. London Gazette 15 June 1916.M.I.D. London Gazette 23 May 1918.Richard Adair Rochfort, whose middle name is sometimes spelled Adare, was born at Dulwich in December 1880, the son of Marcus and Mary Rochfort. His father was a mining engineer in India and returned to Britian just prior to his son's birth, settling at Roslwyn, Lewisham. He himself was married at Forest Hill, Lewisham in 1907, his career listed as farmer.Rochfort entered the war in France on 6 October 1914 with the 1st Battalion, Grenadier Guards in the rank of Serjeant. Detached to serve with the Army Cycling Corps, he was commissioned 2nd Lieutenant on 15 April 1915 with the Royal Inniskilling Fusiliers. Further advanced Captain on 12 October 1915 Rochfort was later transferred again to the Royal Warwickshire Regiment and began to serve attached to the 6th Battalion, Royal Berkshire Regiment.Rochfort was attached to that Regiment when he was awarded his M.C., so it is likely that he joined them at some stage in 1916. They saw action during the taking of the Schwaben Redoubt from 25-27 September before leaving the line over Christmas 1916. Leaving their billets for action in early 1917 they were heavily involved in the Battle of Boom Ravine from 17-18 February, and it was likely for one of these two actions that Rochfort was awarded the M.C.Remaining with the Regiment he was still with them at the opening of the Third Battle of Ypres. They were severely mauled attacking Sanctuary Wood, and during the course of that action one member of the unit, Medical Officer Harold Akroyd, was awarded the Victoria Cross. Their final engagement was at Poelcappelle, starting on 9 October, during which the C.O. Lieutenant-Colonel Longhurst was killed in action. Rochfort succeeded in leading the Battalion into action two days later however his wounds were severe enough his arm was had to be amputated.Despite this injury he remained in service until the end of the war. He was accused of passing a bad cheque in 1923 while Adjutant of the London Regiment, but was subsequently acquitted of the crime. His obituary in the Eastbourne Gazette gives further details to his career stating:'Col. Rochfort, who served with the Grenadier Guards, was responsible for the defence of the Avonmouth docks and Filton aerodrome during the last war.'It goes on to note that Rochfort retired at the end of the Second World War and died at the Royal Victoria Hospital, Netley on 23 July 1954; sold together with copied research.…
A rare campaign group of four awarded to Stoker Petty Officer B. J. Taylor, Royal Navy, who was present for the Battle of Cocos between H.M.A.S. Sydney and S.M.S. Emden on 9 November 1914 whilst loaned to the Royal Australian Navy1914-15 Star (296629 B. J. Taylor, S.P.O., R.N.); British War and Victory Medals (296629 B. J. Taylor. S.P.O. R.N.); Royal Navy L.S. & G.C., G.V.R., 1st issue (296629 B. J. Taylor, S.P.O. H.M.S. Adventure.) together with H.M.A.S. Sydney - S.M.S. Emden Medal 1914, silver, 32mm, presented by the people of Western Australia, named on the reverse (B. J. Taylor. Stoker P’y Off’r) fitted with usual ring for suspension; and H.M.A.S. Sydney - S.M.S. Emden Medal, 9 November 1914, silver Mexican 8 Réales dated ‘1876’, mounted by W. Kerr, Sydney, small chop marks to both sides, this last nearly very fine, otherwise good very fine (6)Benjamin James Taylor was born at Garston, Lancashire on 30 August 1881 and enlisted with the Royal Navy as a Stoker 2nd Class on 14 January 1901. His first service afloat was with Magnificent in July 1901 and he was still with her the next year when advanced Stoker on 18 February 1902. Further advanced Stoker 1st Class on 1 July 1906 and Leading Stoker on 7 September 1911 while stationed with Indus.Transferring to Vivid II Taylor was finally promoted Stoker Petty Officer on 10 September 1912. The next year he was loaned to the nascent Royal Australian Navy on 1 March 1913, arriving at H.M.A. London Depot that same day.Sydney - EmdenTaylor was posted to Sydney on 27 June 1913 and was still with her when the war began as she steamed north to join the battlecruiser H.M.A.S. Australia. They were assigned to the Australian Naval and Military Expeditionary Force which seized New Guinea in September 1914. With the Pacific swiftly secured Australian troops were to be deployed to Egypt and Sydney was ordered to escort the first convoy out in November 1914.At the same time Emden was coming to the end of her epic voyage of destruction through the Indian Ocean. Her next target was the Communications station on the Cocos Islands which she succeeded in knocking out on 9 November, however not before a distress signal was sent. The troop convoy picked up this signal and Sydney was sent out to investigate the disturbance.Newly constructed Sydney had superior speed, armour and firepower to Emden however Captain Jessop was not aware of his opponents' capabilities. As such he agreed with the gunnery officer to open fire at a range of 9,500 yards which he believed to be outside her range. This was not the case however and it was Emden which opened the batting, opening fire and scoring hits on her fourth volley, damaging the aft rangefinders.Emden's only hope was to cause as much damage as possible while the surprise of her attack lasted. However Sydney was in the fight now, the obvious decision would be to use her superior speed to increase the range and batter Emden from afar however the damage to her rangefinders meant that increasing the range would reduce the accuracy of her gunnery. As such she missed with her first two salvoes, destroying Emden's wireless office and her forward gun.As the battle continued Sydney's speed and firepower began to tell, soon destroying the German vessel's steering gear and knocking out a number of guns. Another volley toppled the forward funnel and a shell landed in her aft magazine, forcing the Emden's crew to flood it. Eventually with only one gun still firing, both funnel's collapsed and the engine room ablaze Emden beached on North Keeling Island. Captain Glossop ordered Sydney to ceasefire and signalled the troop convoy 'Emden beached and done for'.Epilogue Taylor continued to serve with Sydney for much of the rest of the war, being returned to the Royal Navy on 23 January 1918. Posted to Adventure on 27 August he saw convoy duty with her until 11 August 1919 and went ashore for the final time. He was finally discharged on 9 June 1922, having earned a war gratuity for his service including the Emden action; sold together with copied service papers.… 25001 SALEROOM NOTICE:Lot is NOT subject to 5% Import Tax.
Sold by Order of the Recipient'We swing between the steel gates to see sabotaged cranes lying toppled and half-immersed in the foul thickness of what was once water - like the skeletons of prehistoric creatures preserved in their death throes...Their only light relief is when they are allowed to blow up the massive stocks of light ammunition left behind by fleeing Iraqis...My team is working just inside the main harbour wall; those not diving or supervising are huddled around a brazier in whatever layers of clothing they can fit over their uniform. They look like a group of down-and-outs surviving inner city decay on an English winter's day.I am met by their CO, Lieutenant Peter Williams, once a carefree Sub Lieutenant with me in Avenger. He now looks drawn and a good deal older - but I dare say so do I. His exploits will rightly win him a Distinguished Service Cross...I inspect their 'goodies', row upon row of Iraqi ordnance: booby traps extracted from dark corners; abandoned shells and grenades; flares and machine-gun bullet bandoliers and weapon cases. They are all stacked neatly into little symmetrical pyramids along the jetty.'Captain Craig brings to life the scenes in the Gulf in Call for FireAn outstanding Gulf War Bomb Disposal 1991 D.S.C. group of twelve awarded to Commander A. P. Williams, Royal Navy, who led Fleet Diving Unit B during Operation 'Granby'He led 'utterly from the front' with a cool confidence to the task, keeping a detailed - and hitherto unpublished - diary of events during those pivotal days and 'personally led several countermining sorties - by day and night - against some of the 1,500 Iraqi mines' and latterly in the post-War efforts in 'appalling and hazardous conditions to clear the Kuwaiti harbours' - thus adding a scarce 'Kuwait' clasp to his laurels for his work commanding Fleet Diving Unit B & NP1037Distinguished Service Cross, E.II.R., the reverse engraved 'Lt A P Williams RN', with its Royal Mint case of issue; Gulf 1990-91, 1 clasp, 16 Jan to 28 Feb 1991 (Lt A P Williams RN); General Service 1962-2007, 1 clasp, Kuwait (Lt A P Williams RN); N.A.T.O. Medal, 1 clasp, Former Yugoslavia; N.A.T.O. Medal, 1 clasp, Kosovo; Jubilee 2002; Jubilee 2012; Royal Navy L.S. & G.C., E.II.R., with 2 Additional Service Bars (Lt Cdr A P Williams DSC RN), with the named box of issue; Oman, Sultanate, Sultan's Commendation Medal (Midal ut-Tawsit), with emblem upon riband; 45th Anniversary National Day Medal; Saudia Arabia, Kingdom, Kuwait Liberation Medal; Kuwait, Emirate, Liberation Medal, silver grade, mounted court-style as worn, these last two separately as per Order of Wear, good very fine, in a case used by the recipient, the lid blocked 'Commander Peter Williams DSC' (12)Approximately 11 D.S.C.s awarded in the post-Second World War era for actions relating to Minewarfare, Diving and EOD work.Just 7 D.S.C.s awarded for Operation 'Granby'.D.S.C. London Gazette 29 June 1991:'Williams arrived in the Northern Arabian Gulf on 1 February 1991 as Deputy Officer in Charge of Fleet Diving Unit B (FDU B). He moved into action immediately, co-ordinating training, refining techniques on new equipment, establishing an Explosive Ordnance Disposal (EOD) cell and overseeing inspections for Improvised Explosive Devices (lEDs) in ships of the RN Task Group as they arrived in Bahrain.During hostilities Williams was the supervisor of an airborne EOD team and of diving operations from Gemini craft, spending many hours in helicopters in the front line of Naval operations, often within ten miles of the enemy coast. Insisting on putting himself in the way of danger before his men, he showed remarkable courage and stamina by leading personally on countermining sorties, placing charges on live buoyant mines and diving for protracted periods, often at night, on live ground mines in order to bring them to the surface for exploitation. In addition he conducted the unenviable task of recovering dead bodies from the sea into helicopters. He led a team of two men on an inspection of HMS Gloucester to search for a mine reportedly entangled in her propeller shafts.Moving ashore on 5 March to Mina Ash Shuaybah he took over as Officer In Charge of FDU B. He established a base camp and helped co-ordinate EOD operations with American and Australian Units for clearing the ports of Mina Al Ahmadi, Mina Ad Dohah and Faylakah Island. The work involved rendering safe unstable live ordnance, beached mines, booby traps and lEDs, clearing buildings and oil tankers of ordnance and collecting dead bodies from the harbour waters. Often these jobs required him and his team to first reach the scene through areas of antipersonnel mines and barbed wire. Throughout this extremely dangerous operation he showed an implacable professionalism and positive leadership which was beyond his experience. At all times his men saw him in the leading role, tirelessly taking on the most hazardous tasks himself.The conditions under which FDU B operated were atrocious. With no infrastructure ashore the men lived in cargo containers on a jetty with no light, sanitation or potable water, in an atmosphere heavy with acrid smoke and toxic fumes from the oilfield fires burning inland, and diving in water with zero visibility due to the thick oil pollution.All the time they were at risk from random gunfire from uncontrolled factions of the local population. Williams's conspicuous leadership, resolute professionalism and boundless energy ensured that his Unit's effectiveness remained at peak levels from start to finish and that his men's morale was of the highest order in the face of dire adversity.'Personel Report covering the dates 1 February-23 April 1991, as Officer in Charge Fleet Diving Unit B & NP1037 to Commander Task Group 321.1, from Commodore C. J. S. Craig, Commander Task Group 321.1:'This is to certify that Lieutenant Williams has conducted himself to my entire satisfaction.Williams came into theatre after two weeks has elapsed of the Gulf War, becoming Deputy Officer in Charge of a Fleet Diving Unit. Initially a supervisor of the airborne EOD teams, he personally led several countermining sorties - by day and night - against some of the 1500 Iraqi mines.Shortly after the war finished he took over he took over as the Officer in Charge of the combined diving team which worked for several weeks in appalling and hazardous conditions to clear the main Kuwaiti harbours - a task which was completed ahead of time and thankfully without any casualties. Throughout this period Williams has led courageously, and utterly from the front, has shown stamina, cheerfulness and professionalism, and has set a fine example to his people. He has briefed clearly, shown economical style with his signalled reports and demonstrated an ability to organise events sensibly and wisely.I have recommended his without reservation for transfer to the General List and would see him developing his professional potential through further command for which I also have recommended him.Altogether Williams can be extremely proud of his achievements in peace and war in the Gulf.'SALE 25001 NOTICE:Now offered together with his Royal Navy Divers Log (Form S. 1627), covering the periods 12 February 1985-8 March 2004, including his Ops during the Gulf War, a terrific resource with a plethora of detail. Further accompanied by his SBS RN Officers MCD Advanced EOD Course Certificate (9 June-25 July 1986) and MCD Officer Qualification Certificate (3 November 1986) and Minewarfare brochure, featuring Williams as OIC FDU2.
The Henley Royal Regatta Grand Challenge Cup Medal, 1908 won by Sir W.A. Akers who rowed as number 2 in the winning Christ Church 8 in 1908, sharing his victory with Apsley Cherry-Garrard, later of Arctic fameA British chemist and industrialist he specialized in physical chemistry and during the Second World War was the director of the Tube Alloys project, a clandestine programme aiming to research and develop British atomic weapons capabilities from 1941 to 1945After the war he was director of research at Imperial Chemical Industries and also served as a member of the Advisory Council of the Department of Scientific and Industrial Research, and the committee that drew up the organisation of what became the United Kingdom Atomic Energy AuthorityRecognising his significant contribution to the war effort he was made a C.B.E. and conferred with a knighthoodHenley Royal Regatta Grand Challenge Cup Medal, 1908, Christ Church engraved on the rim 1908, 'W.A. Akers', additionally engraved on the obverse, 'Christ Church B.C., A.G.B. Cherry-Garrard Bow, 2. W.A. Akers, 3. F.E. Villiers, 4. A.C. Gladstone, 5. G.E. Hope, 6. E. Majolier, 7. H.R. Barker, C.A. Gladstone Str.', in its case of issue, extremely fine[K.B.] London Gazette 28 December 1945.[C.B.E.] London Gazette 31 December 1943.Wallace Alan Akers was born at Walthamstow, Essex in 1888, the son of chartered accountant Charles Akers and his wife,Mary Ethelreda. He was educated at Lake House School in Bexhill-on-Sea, Essex, and Aldenham School. He entered Christ Church, Oxford, where he specialised in physical chemistry, graduating with first class honours in 1909.After university, he joined Brunner Mond & Company in Winnington, Cheshire, as a researcher. In 1924 he joined the Borneo Company, where he served as its general manager in the Far East. He returned to England in 1928 to join Imperial Chemical Industries, into which Brunner Mond had earlier merged. In 1931 he became the chairman of the Billingham division of ICI. This was mainly concerned with the manufacture of ammonia using hydrogen under high pressure, ammonia being one of the company's most profitable products at the time.Between 1933 and 1936 he was involved in a project to produce synthetic petrol from the hydrogenation of coal; ICI executives envisaged competing with oil companies. It became clear that the process would not be competitive but, since it had defence implications, he sought government subsidies. In this he was opposed by Sir John Anderson, the permanent secretary at the Home Office. The change of government following the October 1931 general election brought with it a change in policy and he was able to secure some financial relief.A reorganisation of ICI in 1937 ended Akers' chairmanship of the Billingham division and he was posted to ICI headquarters, where he worked closely with Holbrook Gaskell. At this time, Britain was starting to re-arm. Munitions contracts had begun to roll in, and ICI expanded its production capacity. He became executive manager in 1939.During 1941 Akers was recruited by the British war-time government as director of the Tube Alloys project, a clandestine programme aiming to research and develop British atomic weapons capabilities. This helped galvanize both Britain and America to proceed down a path which led to the Manhattan Project, and ultimately the atomic bombings of Hiroshima and Nagasaki. Historian Margaret Gowing noted that 'No doubt Akers had been picked for his personality and drive that had been considered so important and which he possessed in abundance'.Akers' ICI background led to difficulties when it came to dealing with the American Manhattan Project. American officials such as Vannevar Bush, James Conant and Leslie Groves saw him as "an Imperial Chemical Industries man at heart" and he aroused American suspicions that British interest in atomic energy was with its commercial possibilities after the war. As a result, James Chadwick was appointed the head of the British mission to the Manhattan Project, but Akers remained director of Tube Alloys until the end of the war.In 1946, Akers returned to the Board of ICI where he served as director of research until April 1953, when he retired, having reached the compulsory retirement age of 65. He established university research fellowships and donated money to university laboratories for research purposes. In 1946 he established the Butterwick Research Laboratories to carry out fundamental research, unrelated to commercial objectives. They were later renamed the Akers Research Laboratories in his honour.Akers was made a Commander of the Order of the British Empire in 1944 and was knighted in 1946, both for his services to the war effort. He became a fellow of the Royal Society in 1953 and received honorary degrees of D.Sc. from Durham University and D.C.L. from Oxford University.After his retirement he remained a member of the Advisory Council of the Department of Scientific and Industrial Research and was part of the three-man April 1953 committee that drew up the organisation of what became the United Kingdom Atomic Energy Authority. He was a member of the National Gallery's scientific advisory committee, later becoming a trustee, and was the treasurer of the Chemical Society from 1948 to 1954. He married Bernadette Marie La Marre in 1953 and died at their home in Alton, Hampshire on 1 November 1954.Sold together with a comprehensive obituary for Sir Wallace.For the Distinguished Service Cross and Great War pair awarded to his brother, Lieutenant N.C. Akers, R.N.V.R., please see Lot 309.…
Frontier Light HorseRaised by Lieutenant F. Carrington at King Williams Town, Cape Colony, in 1877. Command soon passed to Major Redvers Buller, K.R.R.C., under whom the F.L.H. served in the final stages of the Ninth War, suffering casualties. In July 1878, the unit, 276 of all ranks, marched from King Williams Town to Pietermaritzburg in Natal, and from there to Sekukuniland in the Transvaal. During September and October the corps saw service against the Sekukini and in November returned to Natal and fought through the Zulu War of 1879 with Wood's Column.At Hlobane on 28 March 1879, the F.L.H. acted as the rear-guard during the withdrawal and subsequently lost nearly 20% of the 156 all ranks engaged. Their Commanding Officer was killed and was succeeded by Captain C. D'Arcy, who on reconnaissance with Sergeant O'Toole would both go on to win the Victoria Cross. The unit was armed with Martini-Henry carbines with a short sword bayonet.478 Medals were awarded to the Frontier Light Horse, 179 of them with clasp '1879'.The Zulu War Medal awarded to Trooper A. Whitecross, Frontier Light Horse, who gallantly saved the life of Trooper Patterson at Hlobane Mountain - for which he was 'mentioned' by Lieutenant-Colonel BullerSouth Africa 1877-79, 1 clasp, 1879 (209, Tpr. A Whitecross, Frontr. L. Horse), very fineAlexander Whitecross was born in Scotland circa 1837 and served with Pulleine's Rangers in 1877-8 before joining the Frontier Light Horse, with whom he served from 14 July 1878-8 August 1879.A good account of his gallantry is offered by Greaves in Crossing the Buffalo:'So steep was the descent down the Devil's Pass that many of Buller's men and horses fell to their deaths; for the survivors, their ordeal was to become even more serious as the Zulus from the main force now reached the lower reaches of the pass and began closing in on both sides. The Zulus began firing at point-blank range into the desperate soldiers while others darted among them, stabbing and spearing to death.Trooper Patterson had managed to lead his horse safely down the pass and had just mounted up when he was speared from his horse leaving him defenceless. As the Zulus closed to kill the injured rider, Trooper Whitecross drove them off by using his rifle as a club. Patterson was hauled to safety and both lived to tell the tale.'His named was 'mentioned' by Lieutenant-Colonel R. H. Buller in the despatches of 29 March 1879.It is understood he served in Prince Alfred's Volunteer Guard during the Basuto Gun War of 1880-81 but died in November 1893 and did not live to claim a Medal (Frontier Light Horse in the Anglo-Zulu War 1879, refers).…
The Africa General Service Medal awarded to District Commissioner H. M. Douglas, Aro Frontier Force, whose long service in Africa saw him thanked by the Secretary of State for his actions during the Ngor Rising and a brace of 'mentions' for fine services in NigeriaAfrica General Service 1902-56, 4 clasps, Aro 1901-1902, S. Nigeria 1902, S. Nigeria 1904, S. Nigeria 1905-06 (Dis: Comr. H. M. Douglas, Aro F.F.), extremely fineM.I.D. London Gazette 23 February & 18 September 1906.Harold Mordey Douglas was born at Sunderland in January 1875, the son of Mordey and Emma Douglas. Joining the Colonial Service in 1894 he served initially as consular agent for Puerto de la Luz, Canary Islands. He was appointed Assistant District Commissioner with the Niger Coast Protectorate in 1897 - the start of a long career in Africa. Whilst in the Protectorate he became involved in organising transport for a cross river-expedition which occurred in 1900.The outbreak of the Anglo-Aro War in 1901 saw Douglas appointed Political Officer with No. 2 column, Aro Field Force. The fighting was surprisingly fierce given the disparity in forces with the city of Arochukwu falling after four days of fighting. The war ended not long after the fall of Bende in the Spring of 1902.Appointed District Commissioner for South Nigeria in 1902, Douglas received the thanks of the Secretary of State for his prompt actions taken in suppressing the Ngor rising in June 1902, earning his South Nigeria 1902 clasp in the process. Again appointed Political Officer to the Imo River expedition, Southern Nigeria in March 1904 he served under the command of then Major Hugh Trenchard.Joining the Bende-Onitsha Hinterland expedition, again as Political Officer, he was 'mentioned' for this service as well as earning the 1905-1906 clasp. The London Gazette on 23 February 1906 states the following of his work there:'After the withdrawal of the Ouitsha Hinterland patrol from the Owerri District, the inhabitants of a small district to the east of Owerri, which had not been visited, refused to allow passage along their roads, and fired on a military escort travelling over one of them. The District Commissioner, Mr. H. M. Douglas, and a small force under Lieutenant Halfpenny, with 86 rank and file, visited the country and met with constant resistance, four soldiers being killed and three wounded before this thickly-populated district submitted.'After the expedition Douglas was appointed Senior District Commissioner in 1906 before transferring to Central Province as Acting Provincial Secretary in 1908-09. His final role was as Acting Assistant Provincial Commissioner and Provincial Secretary of Central Province in 1910-13. Douglas was still living at Warri Province in 1914, he died on 24 May 1926 at the Kapara Estate, Fort Jameson, North-East Rhodesia; sold together with copied extracts from medal rolls, London Gazette entries and other research.Note further information on Douglas can be found in an Article in the O.M.R.S. journal of March 2019 entitled 'Black Douglas'.…
The Waterloo Medal awarded to Private J. Buxton, King's Dragoon Guards, who was killed in action at the Battle of WaterlooWaterloo 1815 (James Buxton, 1st Reg. Dragoon Guards.), slight edge bruise, very fineProvenance:Glendining's, September 1902; December 1915Hayward's Gazette, September 1970Nimrod Dix & Co., 1985.James Buxton was born at Ashover, Derbyshire in 1793 and saw service with the Norfolk Fencible Cavalry. He later joined the King's Dragoon Guards - appearing on their paylist on 25 December 1814 with 1 Troop - with whom he served under the command of Captain William Elton's at the Battle of Waterloo.On that famous day Buxton would have shared in that first great charge of the Household Brigade (1st and 2nd Life Guards, Royal Horse Guards and K.D.G. - 1220 sabres in all) against the 1st and 4th Cuirassiers of Dubois's Brigade. The Brigade was positioned to the rear-centre of the Allied army, directly above the fortified farmhouse of La Haie Sainte. They made a well-executed charge at approximately 2.20pm; French cavalry of the 1st and 4th Cuirassiers had just broken a battalion of Hanoverian infantry and the Household Brigade went forward to counter-attack and save the survivors as best they could.This they achieved but, like their comrades in the Union Brigade, they made the mistake of pursuing their shattered enemy too far thus leaving themselves - on winded horses and on muddy ground - open to counterattack in turn. Consequently, of the 583 officers and men who mounted up that day, 279 (some 48%) were casualties by the end of the battle, including their commanding officer and six other officers.Buxton was one of those killed in action during the Charge, likely during the counter-charge of the French horse. The Prize list for Prize money during Battle of Waterloo and Capture of Paris lists James Buxton DD (discharged dead).Sold together with a copied extract from the Waterloo Records of the 1st (or) King's Dragoon Guards.…
Three: Major C. F. Kelly, 18th Royal Irish Regiment, whose regiment saw heavy fighting during the famous storming of the Shwe-Dagon Pagoda and during the Crimean WarHe was present for the storming of the Redan during which men of the 18th actually breached Sebastopol's defences in an action which won Captain Esmonde the Victoria CrossIndia General Service 1854-95, 1 clasp, Pegu (Lieut. Chas. Fredk. Kelly. 18th. Royal Irish Regt.); Crimea 1854-56, 1 clasp, Sebastopol (Chas. Fredk. Kelly. Capt. 18th. Rl. Irish Regt.) contemporarily engraved naming; Turkish Crimea 1855, Sardinian issue, unnamed as issue, plugged and fitted with an IGS-style suspension bar, edge bruising and light contact marks, very fine (3)Provenance:Dix Noonan Webb, September 2006.Charles Frederick Kelly was commissioned an Ensign in the 18th Regiment on 2 April 1843 and was promoted Lieutenant on 5 February 1847. He served with the regiment in the expedition under General D'Aguilar in April 1847 and was soon to see hot action during the Second Burma War. The unit went into battle for the first time on 5 April at Martaban when they were the first to storm the wall under over of the bombardment. Captain Gillespie is noted as the first in, with the Grenadier Companies and the 80th Regiment in the thick of the action too.Having secured Moulmein, they were again engaged at Rangoon when they assisted the Bengal Sappers and the Bluejackets getting through the thick jungle to bring their ladders onto the White House stockade. On 14 April they were faced with the magnificent Shwe-Dagon pagoda. A fiercely protected bastion, the spectacular 14th century pagoda was defended by cannon over its three main tiers, in addition to being protected by a brick and mud rampart. The force chosen to storm the Pagoda comprised a detachment of the 80th, two Companies of the 18th (Royal Irish) Regiment and some troops from 40th Bombay Native Infantry. An approach march having been made before dawn through jungle, the ranks of the storming party readied themselves for the attack. James Jones's History of the South Staffordshire Regiment (1705-1923) takes up the story:'The distance to be covered in the advance to the eastern entrance of the Pagoda was 800 yards. The troops crossed steadily under a heavy fire from the walls crowded with the enemy. When the storming party reached the Pagoda steps, a rush was made for the upper terrace, and a deafening cheer told that the Pagoda was won. The enemy evacuated the place in great confusion, and were severely handled by the troops and the fire from the steamers on the river.They latterly found themselves under siege at Prome in August-October 1852 and in November two Companies were sent out to the districts on patrol to locate enemy. With a force cornered at Tomah, the British waited until March 1853 for reinforcements for a full scale attack, which eventually cost the 18th 1 killed and 28 wounded. The Regiment sent Companies onto the Tonghoo Pass to shepherd a delivery of 148 elephants over the pass. Others were sent out against Myat Toon and were part of the main attack on his stronghold on 19 March, when a frontal attack with the Sikhs secured the victory. Once peace stopped the field operations, the unit was returned to Calcutta, depleted by 365 casualties over the course of the operations.'Promoted to Captain on 4 August 1854 Kelly was to serve at Sebastopol from December 1854. Whilst there the Regiment took part in the first storming of the Redan on 18 June 1855 after a heavy bombardment the night before. Unfortunately the famous Russian engineer, Totleben, was able to repair the damage during the night which- combined with a number of mis-communications between the allies- saw the attack repulsed. In the course of this the Royal Irish suffered losses of 259 killed and wounded.Part of the reason for such high losses was their surprise success, breaking through into Sebastopol itself, the famous War Correspondent William Russell noted:'The moment the enemy retreated, their batteries opened a heavy fire on the place from the left of the Redan and from the Barrack battery. Four companies of the XVIIIth at once rushed out of the cemetery towards the town, and actually succeeded in getting possession of the suburb. Captain Hayman was gallantry leading on his company when he was shot through the knee. Captain Esmonde followed, and the men, once established, prepared to defend the houses they occupied.'For his gallantry Esmonde was awarded the Victoria Cross, the Regiment however had still been decimated in the fighting. Kelly was advanced Major on 14 December 1860; sold together with copied research.… 25001 SALEROOM NOTICE:Lot is NOT subject to 5% Import Tax.
Pair: Midshipman J. H. Woodhouse, Royal NavyBritish War and Victory Medals (Mid. J. H. Woodhouse. R.N.), good very fine (2)John Herbert Woodhouse - or Jack to his friends and comrades - was born in 1900. Aged twelve, he was sent to the Royal Naval College for two years, then to Dartmouth College in 1914. Appointed Midshipman aboard St Vincent, he served in that rank during the Great War and saw two of his elder brothers perish during the conflict. His father petitioned the Admiralty that he be released from service, this being confirmed in a letter dated 18 December 1918.Woodhouse went out to India as an engineer on Tea Plantations in Assam; sold together with copied research including a series of letters, including his near-death experience whilst on a Tiger hunt in 1924.…
The 'Trench Raid Leader's' M.C. group of three awarded to Lieutenant P. Crampton, 2/5th Battalion, Loyal North Lancashire Regiment, who was seriously wounded during a hand-to-hand clashThe same action saw him seriously wounded while leading a bayonet charge, leading to Crampton being treated by Harold Gillies, one of the pioneers of modern plastic surgeryMilitary Cross, G.V.R., unnamed as issued; British War and Victory Medals (Lieut. P. Crampton.), good very fine (3)M.C. London Gazette 16 August 1917, the original citation states:'For conspicuous gallantry and devotion to duty. He commanded a raid on the enemy trenches. Previously he had done most valuable reconnaissance work, entering the enemy lines on previous occasions. The success of the raid was largely due to his fine patrol work beforehand.'Percy Crampton enlisted initially with the Inns of Court Officer Training Regiment and was Commissioned 2nd Lieutenant from that unit on 15 September 1915. Posted to the Loyal North Lancashire Regiment he was later advanced Lieutenant on 27 July 1915. The Battalion entered the war in Flanders on 8 February 1917 with the 55th Division stationed in the Cordonnerie Sector. Their first actions were largely trenches raids launched across the lines, starting in May 1917, one of these was commanded by Crampton, the Regimental History outlines this stating:'Another raid, but on a smaller scale, took place on the 24th, when two officers- Lieutenants Crampton and Marshall- and fifteen men started off. These had just reached the enemy's support line when a German patrol was heard approaching, and the raiders divided into two parties; one charged the enemy with the bayonet and a sharp fight ensued, two Germans being killed and four captured; two of these last were wearers of the Iron Cross ribbons and all looked very fit and in good condition. Of the raiding party only one- Lieutenant P. Crampton- was wounded.'This is added too by several newspaper articles, one of which entitled 'Plucky Officer Wounded on Raiding Party' states:'From an account received by Mr. Crampton of the incident which resulted in the casualty it appears that Lieutenant Crampton and another officer, accompanied by seven men, took part in a raid on the enemy's lines. In an encounter at close quarters with six of the enemy. Lieutenant Crampton was wounded in the neck and shoulder, it is thought, by revolver fire. Two of the enemy were, however, killed, and the remainder surrendered, the whole party of six thus being accounted for. The Boches' arms and equipment, which had been thrown down, were collected and the prisoners hurried down to the enemy front line, and across No Man's Land to the British lines. It is stated that two, at least, of the Boches were wearing the ribbon of the Iron Cross; one was also wearing a Red Ribbon. Lieutenant Crampton was able to reach his own lines, with assistance, and was quickly put on a stretcher and brought to a dressing station, where first aid was given him.Has done Good Work in France.In a letter to Mr. Crampton, the Commanding Officer of the Battalion writes as follows:- "Your son was wounded severely, but I hope and trust he will be all right. He was very brave over it. He has done good work in France and some weeks back, when my second in command was killed, carried another officer out of the shelled area on his back. This, I know, will be a comfort to you. You will get news when he reaches England, and I trust you will let me know how he progresses."Lieutenant Crampton is 26 years of age and was educated at the Warrington Grammer School. At the age of 21 he was articled as a solicitor, and, up to his joining the Army, was in practice with his uncle, who is a solicitor in Leigh. Yesterday Mr. Crampton was greatly relieved to hear that his son was making satisfactory progress.'Returning to Britain, Crampton's serve injuries were treated by Harold Gillies, a New Zealand born medical officer and one of the pioneering forces behind plastic surgery. After seeing skin grafting techniques in France and America Gillies opened a ward in Cambridge where he began to develop the techniques required to treat facial injuries. Here he performed what is believed to be the first modern plastic surgery on Walter Yeo, who was wounded at the Battle of Jutland.Gillies treatment of Crampton appears to have been for a wound to the jaw, a transcript of his medical record notes 'Fractured Mandible' and 'Keloid Scar Clavicle'. The results of these surgeries are unclear however Crampton certainly survived, going on to work as a solicitor for his uncle T. R. Dootson.During the Second World War he was living near Leigh and joined the Newchurch Local Defence Volunteers. A newspaper article from the time- - in a scene that could have been called straight out of Dad's Army - makes reference to him being asked to resign after an argument with the local Rector. Rather touchingly it is related that eighty members of the L.D.V. threatened to resign if Crampton was forced out of his post; sold together with copied research.…



































!['The C.O., Michael, and John had each destroyed an Me. 110, while Mac [McArthur] shot down two Junkers 87 dive-bombers. He wo](https://cdn.globalauctionplatform.com/5d973dee-439b-4cad-a633-b2b500cc4fbb/4792aa89-82b0-47d2-ad06-b2b500d55c86/468x382.jpg)